예외 처리
- 널널한 개발자님의 독하게 시작하는 Java Part 2에서 에러와 예외의 개념, Checked/Unchecked 예외의 차이, try-catch-finally 구문 사용법, 예외 클래스 계층 구조, throws를 이용한 예외 전파, 그리고 사용자 정의 예외 작성 방법을 정리함
에러의 정의
에러(Error)란?
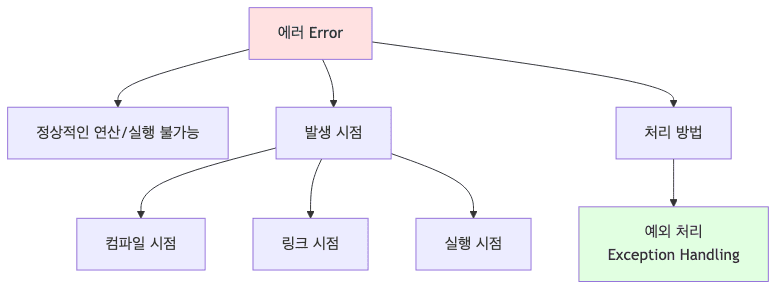
- 기본 개념
- 정상적인 연산/실행이 불가능한 상황
- 예외 상황으로 정의하여 별도 처리
- 프로그램 흐름을 계속 이어갈 수 있음
Error와 Exception
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
// Error - 프로그램이 복구할 수 없는 심각한 문제
try {
// OutOfMemoryError 발생 가능
int[] huge = new int[Integer.MAX_VALUE];
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
// 잡을 수는 있지만, 일반적으로 복구 불가능
// Error는 catch하지 않는 것이 관례
}
// Exception - 프로그램이 복구할 수 있는 문제
try {
FileReader reader = new FileReader("data.txt");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// 복구 가능: 기본 파일 사용, 사용자에게 재입력 요청 등
}
- Error
- JVM이나 시스템 레벨의 심각한 문제 (복구 불가능)
OutOfMemoryError,StackOverflowError,VirtualMachineError- 일반적으로 catch하지 않음
- Exception
- 애플리케이션 레벨의 문제 (복구 가능)
- Checked
- 복구 가능한 예외
- Unchecked
- 프로그래밍 오류
if문으로 예외 처리 시 단점
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
public class FileProcessor {
public void process(String filename) {
File file = new File(filename);
// 단계 A: 파일 존재 확인
if (!file.exists()) {
handleError1();
return;
}
// 단계 B: 파일 읽기 권한 확인
if (!file.canRead()) {
handleError2();
return;
}
// 단계 C: 파일 열기
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
handleError3();
return;
}
// 단계 D: 파일 읽기
if (fis != null) {
try {
int data = fis.read();
} catch (IOException e) {
handleError4();
return;
}
}
}
}
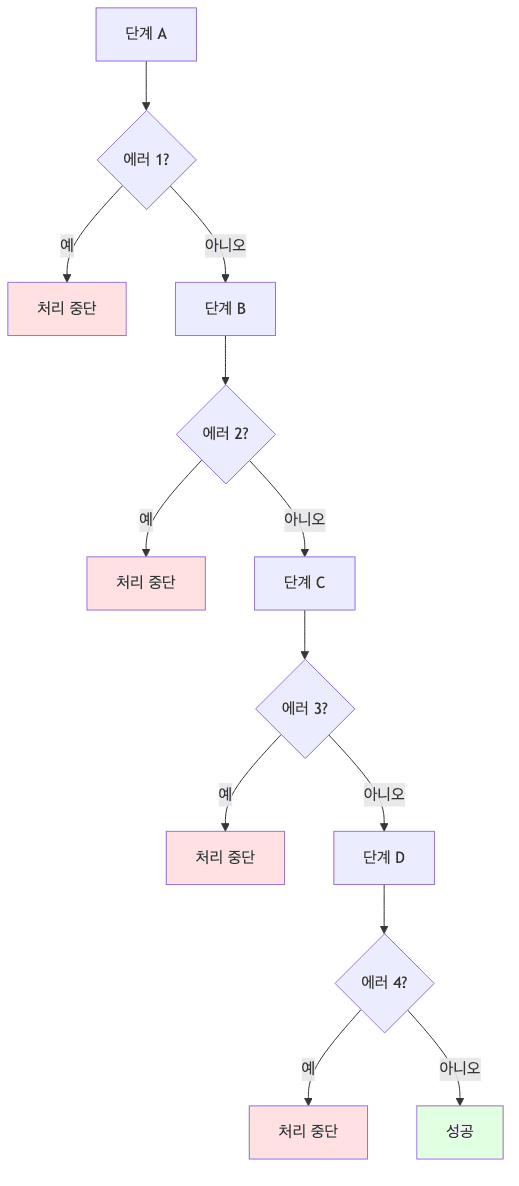
- 문제점
- 코드가 복잡해짐
- 정상 흐름과 에러 처리가 섞임
- 가독성 저하
- 에러 처리 로직이 중복될 수 있음
예외 처리의 장점
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
public class FileProcessor {
public void process(String filename) {
try {
// 정상 흐름만 기술 (가독성 올라감)
File file = new File(filename);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
int data = fis.read();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
handleFileNotFound(e);
} catch (IOException e) {
handleIOError(e);
} finally {
cleanup();
}
}
}
- 정상 흐름과 예외 처리 분리
- 코드 가독성 향상
- 예외 처리를 통합하여 관리
예외 종류
Checked와 Unchecked
Checked Exception
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
// Exception을 직접 상속
public class MyCheckedException extends Exception {
public MyCheckedException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
public class FileManager {
// throws 필수
public void readFile(String path) throws IOException {
FileReader reader = new FileReader(path);
}
public void process() {
// 반드시 예외 처리 필요
try {
readFile("data.txt");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Exception을 직접 상속 (RuntimeException제외)- 컴파일 타임에 체크
- 반드시 처리 또는 throws 선언 필요
IOException,SQLException,ClassNotFoundException
Unchecked Exception (Runtime Exception)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
// RuntimeException 상속
public class MyRuntimeException extends RuntimeException {
public MyRuntimeException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
public class Calculator {
// throws 선언 불필요
public int divide(int a, int b) {
if (b == 0) {
throw new ArithmeticException("0으로 나눌 수 없음");
}
return a / b;
}
public void process() {
int result = divide(10, 0);
}
}
RuntimeException을 상속- 런타임에 발생
- 예외 처리 강제하지 않음
NullPointerException,ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
Checked와 Unchecked 비교
| 구분 | Checked | Unchecked |
|---|---|---|
| 상속 | Exception | RuntimeException |
| 체크 시점 | 컴파일 타임 | 런타임 |
| 처리 강제 | 필수 (try-catch 또는 throws) | 선택 |
| 사용 목적 | 복구 가능한 예외 | 프로그래밍 오류 |
| 예시 | IOException, SQLException | NullPointerException, IllegalArgumentException |
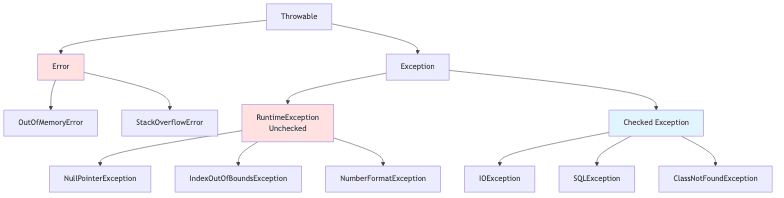
예외 클래스 계층 구조
전체 구조
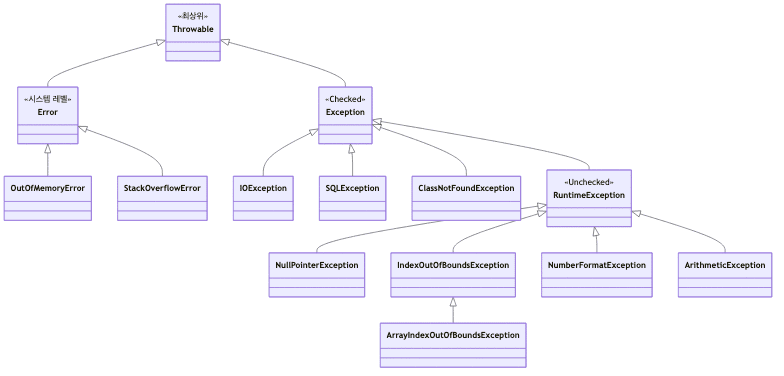
대표적 런타임 예외
NullPointerException
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public class NPEExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = null;
// NullPointerException 발생
int length = str.length();
// 올바른 처리
if (str != null) {
int safeLength = str.length();
}
}
}
- 발생 원인
- 대상 인스턴스가 존재하지 않는(null) 참조자로 멤버 접근
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public class ArrayException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 발생
int value = numbers[10];
// 올바른 처리
if (10 < numbers.length) {
int safeValue = numbers[10];
}
}
}
- 발생 원인
- 배열의 인덱스 범위를 벗어나는 접근
NumberFormatException
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public class NumberException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String text = "abc123";
// NumberFormatException 발생
int number = Integer.parseInt(text);
// 올바른 처리
try {
int safeNumber = Integer.parseInt("123");
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("숫자 형식이 아닙니다");
}
}
}
- 발생 원인
- 숫자로 변환할 수 없는 문자열을 변환 시도
ClassCastException
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public class CastException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object obj = "문자열";
// ClassCastException 발생
Integer number = (Integer) obj;
// 올바른 처리
if (obj instanceof Integer) {
Integer safeNumber = (Integer) obj;
}
}
}
- 발생 원인
- 잘못된 하향 형변환 (Downcasting)
보편적 예외 사례
File I/O
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
import java.io.*;
public class FileIOExample {
public void readFile(String path) throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(path));
String line = reader.readLine();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.err.println("파일을 찾을 수 없습니다: " + path);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("파일 읽기 오류: " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
- 발생 가능한 예외
FileNotFoundException- 파일 미존재
IOException- 읽기 권한 없음, 디스크 오류
SecurityException- 보안 정책에 의한 접근 차단
Network I/O
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class NetworkExample {
public void connect(String host, int port) {
Socket socket = null;
try {
socket = new Socket(host, port);
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
System.err.println("호스트 연결 실패: " + host);
} catch (ConnectException e) {
System.err.println("서버 연결 거부");
} catch (SocketTimeoutException e) {
System.err.println("연결 시간 초과");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("네트워크 오류: " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if (socket != null) {
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
- 발생 가능한 예외
- 호스트 통제 불가능 요소
- 방화벽, IPS, WAF 정책
- 네트워크 단절
Database I/O
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
import java.sql.*;
public class DatabaseExample {
public void query(String sql) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost/mydb", "user", "pass"
);
stmt = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.err.println("DB 오류: " + e.getMessage());
System.err.println("SQL State: " + e.getSQLState());
System.err.println("Error Code: " + e.getErrorCode());
} finally {
try {
if (stmt != null) stmt.close();
if (conn != null) conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
- 발생 가능한 예외
- SQL 문법 오류
- 연결 끊김
- 권한 부족
try-catch-finally 구문
기본 문법
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
try {
// 예외가 발생할 수 있는 코드
} catch (ExceptionType1 e) {
// ExceptionType1 처리
} catch (ExceptionType2 e) {
// ExceptionType2 처리
} finally {
// 항상 실행되는 코드 (선택 사항)
}
기본 사용 예제
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
public class TryCatchExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] numbers = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
try {
numbers[0] = 100;
System.out.println(numbers[0]);
// ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 발생
numbers[5] = 500;
System.out.println("try 블록 끝");
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
System.out.println("런타임 예외 발생");
} finally {
System.out.println("항상 실행됨");
}
System.out.println("프로그램 계속 실행");
}
}
-
출력 결과
1 2 3 4
100 런타임 예외 발생 항상 실행됨 프로그램 계속 실행
다중 catch
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
public class MultipleCatchExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
String text = args[0];
int number = Integer.parseInt(text);
int result = 100 / number;
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("인자가 제공되지 않았습니다");
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("숫자 형식이 아닙니다");
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("0으로 나눌 수 없습니다");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("알 수 없는 오류: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
- catch 순서 규칙
- 구체적인 예외를 먼저
- 일반적인 예외를 나중에
Exception은 가장 마지막
NullPointerException 처리
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
public class NullPointerExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int input = scanner.nextInt();
Shape shape = null;
if (input == 0) {
shape = new Rectangle();
} else if (input == 1) {
shape = new Triangle();
}
try {
shape.render();
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("오류: 도형이 생성되지 않았습니다");
}
}
}
finally 블록의 특징
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public class FinallyExample {
public static int testFinally() {
try {
return 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
return 2;
} finally {
System.out.println("finally 실행");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result = testFinally();
System.out.println("결과: " + result);
}
}
-
출력 결과
1 2
finally 실행 결과: 1
-
특징
- 항상 실행됨 (
return,break,continue있어도) - 자원 정리에 주로 사용
- 항상 실행됨 (
finally블록에서의 return문 사용
try/catch블록의return값이 무시되거나 발생한 예외가 덮어씌워질 수 있으므로return을 사용하지 않음
사용자 정의 예외
Runtime Exception
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
// 사용자 정의 런타임 예외
public class MyRuntimeException extends RuntimeException {
private String errorMessage;
public MyRuntimeException(String message) {
super(message);
this.errorMessage = message;
}
public String getErrorMessage() {
return errorMessage;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public class ShapeRenderer {
public void render(Shape shape) {
if (shape == null) {
throw new MyRuntimeException("도형이 null입니다");
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
System.out.print("* ");
}
System.out.println();
}
throw new MyRuntimeException("렌더링 테스트 메시지");
}
}
중첩 try-catch
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
public class NestedTryCatchExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int input = scanner.nextInt();
Shape shape = null;
if (input == 0) {
shape = new Rectangle();
} else if (input == 1) {
shape = new Triangle();
}
try {
try {
shape.render();
} catch (MyRuntimeException e) {
System.out.println(e.getErrorMessage());
}
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("오류: NullPointer");
}
}
}
throws를 이용한 예외 전파
기본 개념
Checked Exception과 throws
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
// Checked 예외 정의
public class MyCheckedException extends Exception {
private String message;
public MyCheckedException(String msg) {
this.message = msg;
}
public String getMsg() {
return message;
}
}
throws 선언 필수
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public class ThrowsExample {
// throws 선언 필수
static void checkValue() throws MyCheckedException {
int value = 110;
if (value < 0 || value > 100) {
throw new MyCheckedException("값이 범위를 벗어났습니다");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 컴파일 에러 발생
checkValue();
}
}
-
컴파일 에러
1 2
unreported exception MyCheckedException; must be caught or declared to be thrown
try-catch 처리 방법
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public class ThrowsExample {
static void checkValue() throws MyCheckedException {
int value = 110;
if (value < 0 || value > 100) {
throw new MyCheckedException("값이 범위를 벗어났습니다");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
checkValue();
} catch (MyCheckedException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMsg());
}
}
}
throws 전파 처리 방법
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
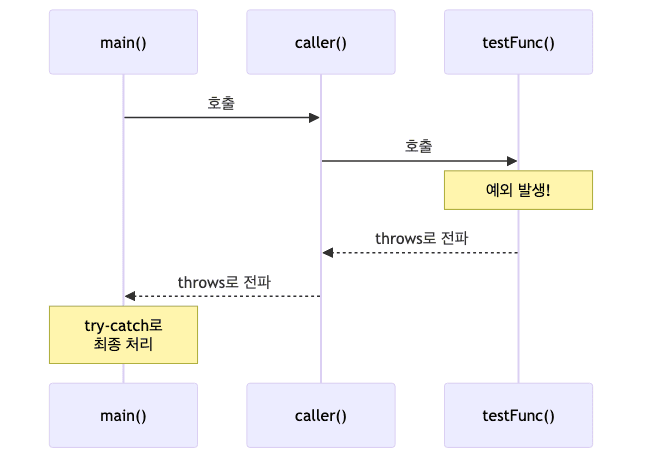
public class ThrowsChainExample {
static void checkValue() throws MyCheckedException {
int value = 110;
if (value < 0 || value > 100) {
throw new MyCheckedException("값이 범위를 벗어났습니다");
}
}
// throws로 예외 전파
static void caller() throws MyCheckedException {
checkValue();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
caller();
} catch (MyCheckedException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMsg());
}
}
}
throws 전파 흐름

예외 처리 권장 가이드
구체적인 예외 처리
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
try {
// ...
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// 파일 없음 처리
} catch (IOException e) {
// IO 오류 처리
} catch (Exception e) {
// 예상치 못한 오류
}
예외 무시하지 않기
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
try {
riskyOperation();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("작업 실패", e);
}
// 합법적으로 예외를 무시하는 경우 (드물지만 존재)
try {
loadOptionalConfig();
} catch (IOException expected) { // 변수명을 expected로 하여 의도 명시
// 선택적 설정 파일 없음 - 기본값 사용
logger.debug("Optional config not found, using defaults");
}
자원 정리 (try-with-resources)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
// try-with-resources (Java 7+)
// AutoCloseable 인터페이스를 구현한 객체만 사용 가능
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("data.txt"))) {
// 블록을 벗어나면 자동으로 close() 호출됨
// ...
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 복수 자원 처리 및 Java 9+ 문법
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("in.txt");
try (fis; // 외부 변수 사용 (Java 9+)
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("out.txt")) {
// 리소스 사용...
} catch (IOException e) {
// 예외 처리
}
예외 변환과 체이닝
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public class DataService {
public Data getData(int id) throws DataServiceException {
try {
return database.query(id);
} catch (SQLException e) {
// 원본 예외(e)를 cause로 전달해야 스택 트레이스가 유지됨
throw new DataServiceException("데이터 조회 실패: " + id, e);
}
}
}
연습 문제
-
예외 처리 강제성 측면에서, 체크 예외와 언체크 예외의 주요 차이는 무엇인가요?
a. 체크 예외는 컴파일 시점에 처리 강제성을 가지며, 언체크 예외는 그렇지 않습니다
- 체크 예외는 컴파일러가 처리 강제성을 가져서 코드 수정이 필요하지만, 언체크 예외(런타임 예외)는 명시적 처리가 필요 없음
- 안정성 향상에 기여를 함
-
예외 처리를 위해
try-catch-finally구문을 사용할 때,try블록의 역할은 무엇인가요?a. 예외 발생 가능성이 있는 코드를 감싸는 영역입니다.
try블록은 예외가 발생할 수 있는 코드 구문을 묶어주는 역할을 함- 정상적인 흐름과 예외 상황을 분리하여 코드를 구조화하는 데 도움을 줌
-
try블록에서 예외가 발생했을 때, 어떤 코드가 실행되도록 하려면 어떤 블록을 사용해야 합니까?- a.
catch catch블록은try블록에서 발생한 예외를 받아 처리하는 역할을 함- 다양한 예외 종류마다 여러 개의
catch블록을 사용할 수 있음
- a.
-
try-catch-finally구문에서,finally블록에 작성된 코드는 언제 실행이 보장되나요?- a.
try또는catch블록 실행 후, 예외 발생 여부와 관계없이 항상 실행됩니다 finally블록은try블록의 코드가 정상적으로 완료되든,catch블록에서 예외가 처리되든 상관없이 항상 실행됨- 자원 해제 등에 유용하게 사용됨
- a.
-
메서드 선언부에
throws키워드를 사용하여 예외를 명시하는 것은 주로 어떤 영향을 미치나요?- a. 해당 메서드를 호출하는 코드가 예외 처리 하거나 다시
throws로 위임해야 함을 강제합니다 throws는 메서드에서 발생 가능한 예외를 호출자에게 알리고 처리를 위임함- 특히 체크 예외의 경우 호출자가
try-catch로 처리하거나 다시throws해야 함
- a. 해당 메서드를 호출하는 코드가 예외 처리 하거나 다시
정리
- 에러는 정상적인 연산/실행이 불가능한 상황을 의미하며 예외 처리를 통해 프로그램 흐름을 유지할 수 있음
- 예외 처리는 정상 흐름과 에러 처리를 분리하여 코드 가독성을 향상시킴
- Checked Exception(체크 예외)은 컴파일 타임에 체크되며 반드시 처리하거나
throws로 선언해야 함 - Unchecked Exception(언체크 예외)은 런타임에 발생하며 예외 처리가 강제되지 않음
NullPointerException,ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException,NumberFormatException,ClassCastException등이 대표적인 런타임 예외임- File I/O, Network I/O, Database I/O 작업 시 다양한 예외가 발생할 수 있으며 적절히 처리해야 함
try-catch-finally구문을 통해 예외를 처리하며,finally블록은 항상 실행됨- 다중
catch블록 사용 시 구체적인 예외를 먼저, 일반적인 예외를 나중에 배치해야 함 - 사용자 정의 예외는
Exception또는RuntimeException을 상속하여 생성할 수 있음 throws키워드를 통해 예외를 호출자에게 전파할 수 있음- 예외 처리 시 구체적인 예외를 잡고, 예외를 무시하지 않으며, 자원을 적절히 정리해야 함
- Java 7+에서는
try-with-resources를 사용하여 자원을 자동으로 정리할 수 있음 - 예외는 빨리 발생시키고 늦게 잡는 것이 원칙임