학습 개요
- 멀티 스레드 프로그램을 작성하는 방법과 스레드의 실행 과정을 이해함
- 여러 스레드가 동시에 수행될 때 스레드 간의 협업을 위해 스레드를 제어하는 메소드가 필요함
- 스레드 간의 상태 변화와 함께 스레드 제어 메소드를 학슴함
- 여러 스레드가 동일 자원에 접근할 때 반드시 필요한 동기화 방법을 살펴 봄
학습 목표
- 멀티 스레드 프로그램의 실행 과정을 설명할 수 있음
- 스레드를 생성하고 시작시키는 프로그램을 작성할 수 있음
- 스레드의 상태 변화와 상태 제어 메소드를 설명할 수 있음
- 스레드를 동기화 시키는 프로그램을 작성할 수 있음
강의록
프로세스와 스레드
프로세스와 스레드
- Java 프로그램은 하나의 프로세스로 만들어져 실행됨
- 프로세스는 프로그램의 통상적 실행 단위
- 프로세스는 자원을 확보하고 있는 실행 중인 프로그램
- 지금까지는 프로세스에서 하나의 스레드가 생성되고,
main()메소드가 호출되어 실행됨(단일 스레드)
- 지금까지는 프로세스에서 하나의 스레드가 생성되고,
- 스레드는 프로세스 내에 존재하는 소규모 실행 흐름
- 하나의 프로세스 내에 여러 스레드가 동시에 실행될 수 있음
- 스레드는 경량 프로세스
멀티 스레드
- 하나의 프로세스 내에서 동시 실행을 위해 존재하는 여러 스레드
- Java 프로그램은 하나의 스레드(
main스레드)로 시작됨main스레드에서 자식 스레드를 만들고 시작 시킬 수 있음- 그러면 여러 스레드가 동시에 독립적으로 실행되고 종료됨
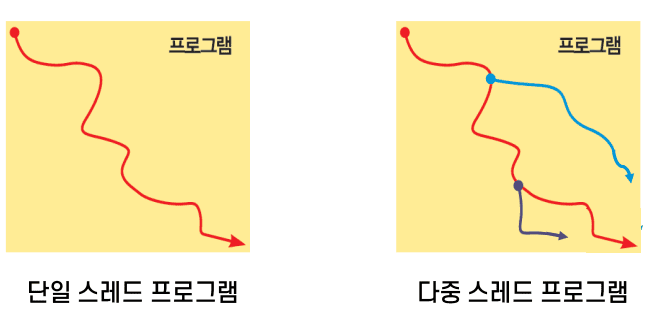
스레드의 생성
Thread클래스
- 스레드의 생성과 관리를 위한 메소드를 제공
- 스레드 생성을 위해
Thread클래스의 객체가 필요함 -
주요 생성자
생성자 설명 Thread()새로운 스레드를 생성하며, 이름이 Thread-n으로 자동으로 주어짐 Thread(String name)새로운 스레드를 생성하며, 스레드의 이름을 name으로 지정 Thread(Runnable target)새로운 스레드를 생성하며, 스레드의 이름이 자동으로 주어짐, 스레드가 실행될 때 target 객체의 run()메소드가 실행됨Thread(Runnable target, String name)스레드의 이름을 name으로 지정하며, 나머지는 위와 같음 -
주요 메소드
메소드 설명 static Thread currentThread()현재 실행 중인 스레드 객체의 참조 값을 리턴 String getName()this스레드의 이름을 리턴void setName(String name)this 스레드의 이름을 name으로 변경int getPriority()this스레드의 우선 순위를 리턴void setPriority(int newPriority)this스레드의 우선 순위를 newPriority로 변경void start()run()을 호출하여this스레드를 실행시킴
스레드의 생성과 실행
Thread유형의 객체t를 생성t.start()를 호출- 스레드의 실행이 시작됨
- 이것은
run()메소드를 호출하는 것 void run()메소드에 스레드의 실행 코드가 있음
run()메소드를 정의하는 두 가지 방법이 있음- 또는
Thread객체를 생성하여 실행시키는 두 가지 방법
- 또는
스레드 실행 방법 1 - Thread클래스를 상속 받는 클래스
Thread클래스를 상속 받는 클래스 A를 정의- 여기서
void run()메소드를 재정의
- 여기서
-
A 유형의 객체를 생성하고
start()를 호출함1 2 3 4 5 6
class MyThread extends Thread { public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) System.out.println(getName()); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
public class Main { public static void main(String args[]) { Thread t1 = new MyThread(); t1.start(); Thread t2 = new MyThread(); t2.start(); System.out.println("main"); } } // Thread-0 // Thread-0 // Thread-1 // Thread-1 // main // Thread-1 // Thread-1 // Thread-1 // Thread-1 // Thread-1 // Thread-1 // Thread-1 // Thread-1 // Thread-0 // Thread-0 // Thread-0 // Thread-0 // Thread-0 // Thread-0 // Thread-0 // Thread-0
스레드 실행 방법 2 – Runnable인터페이스를 구현한 클래스
Runnable인터페이스를 구현한 클래스 B를 정의- 여기서
void run()메소드를 구현
- 여기서
Thread객체를 생성할 때, B 객체Runnable객체를 인자로 사용-
start()를 호출함1 2 3 4 5 6
class MyThread implements Runnable { public void run( ) { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread t1 = new Thread(new MyThread(), "thd0"); t1.start(); Thread t2 = new Thread(new MyThread(), "thd1"); t2.start(); System.out.println("main"); } } // main // thd0 // thd0 // thd1 // thd1 // thd1 // thd1 // thd1 // thd1 // thd0 // thd0 // thd1 // thd1 // thd1 // thd1 // thd0 // thd0 // thd0 // thd0 // thd0 // thd0
멀티 스레드의 실행
- 멀티 스레드 프로그램의 실행 결과는 예측할 수 없음
- 실행 결과가 매번 다를 수 있음
- 각 스레드는 정해진 순서 없이 독립적으로 실행 됨
-
main스레드는 다른 스레드를 시작시키나, 다른 스레드의 실행과 무관하게 실행 되고 종료 됨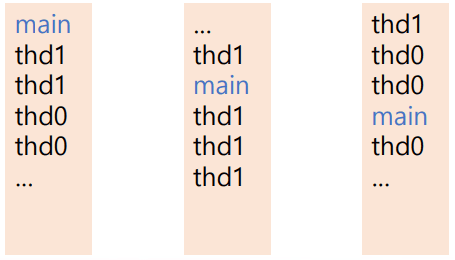
스레드 제어하기
스레드의 상태
-
생성 된 스레드가 CPU를 얻어 실행되고 최종적으로 종료될 때까지 여러 상태 변화를 겪음
메소드 설명 Startable객체가 생성되었으나 start()의 실행 전Runnablestart()메소드가 호출되었으나 CPU 획득 전RunningCPU를 얻어 실행 중 Not RunningCPU를 잃고 중단 된 상태, Blocked, Waithing, Timed_Waiting Deadrun()메소드가 종료 된 상태
스레드의 상태 전이
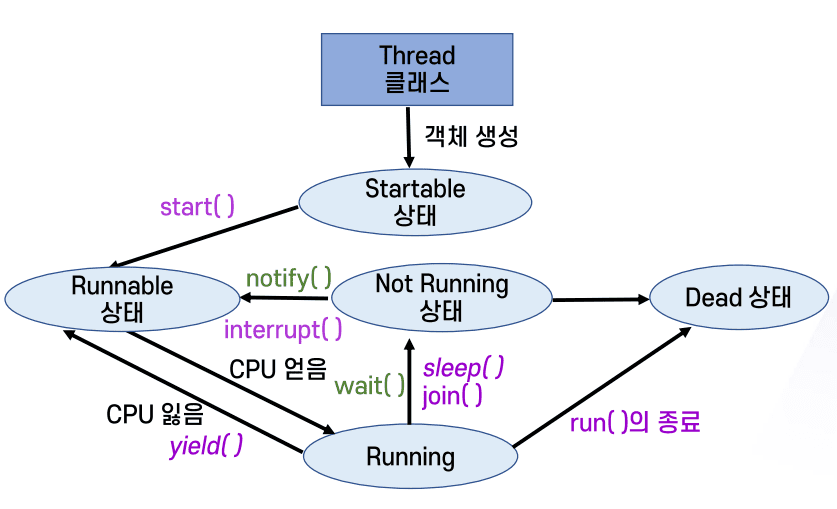
스레드의 상태 제어를 위한 메소드
void setPriority(int newPriority)- 스레드의 우선 순위를 변경
- 높은 우선 순위를 가지는 스레드가 CPU를 얻을 확률이 높음
static void sleep(long millis) throws InterruptedException- 현재 실행 중인 스레드가 정해진 시간 동안 실행을 멈추고 Not Running 상태로 들어감
- 다른 스레드가 이 스레드를
interrupt()메서드를 통해 깨우면InterruptedException예외가 발생함
static void yield()- 현재 실행 중인 스레드가 잠시 실행을 멈추고 Runnable 상태로 들어감
- CPU를 다른 스레드에게 양보하는 것
void join() throws InterruptedException- 스레드가 종료될 때까지 기다림
- 현재 실행 중이었던 스레드는 Not Running 상태로 들어감
void join(long millis)- 최대 millis 시간 동안 기다림
- 기다리는 중에 다른 스레드가 이 스레드를 깨우면
InterruptedException을 받으면서 리턴 됨
void interrupt()- 스레드를 인터럽트 시킴
- 스레드가
wait(),join(),sleep()에 의해 중단된 상태였다면 그 상태에서 깨어나Runnable상태가 됨
스레드 상태 제어를 위한 Object클래스의 메소드
void wait() throws InterruptedException- 객체를 처리 중인 스레드가 대기 상태로 감
- 다른 스레드가 해당 객체에 대해
notify()메서드를 호출할 때까지 기다림
void wait(long millis) throws InterruptedException- 객체를 처리 중인 스레드가 정해진 시간 동안 대기 상태가 됨
- 다른 스레드가 해당 객체에 대해
notify()메서드를 실행시켜 주면 대기 중이라도 이 스레드가 깨어날 수 있음 - 이 메서드는
synchronized메서드의 내부에서만 호출 가능
void notify()wait()를 호출하여 대기 중인 스레드를 깨워 줌- 이 메서드는
synchronized메서드의 내부에서만 호출 가능
스레드의 상태 제어 예
-
yield()로 제어하기1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
class MyThread implements Runnable { public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { String thd_name = Thread.currentThread().getName(); System.out.print(thd_name + " "); if (thd_name.equals("thd1")) Thread.yield(); } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34
public class Main { public static void main(String args[]) { Thread my_thread1 = new Thread(new MyThread(), "thd1"); Thread my_thread2 = new Thread(new MyThread(), "thd2"); my_thread1.start(); my_thread2.start(); } } // thd1 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 // thd1 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 // thd1 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd1 thd1 thd2 // thd2 thd1 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 // thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 // thd2 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 // thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 // thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 // thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 // thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 // thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 thd2 // ... ... // thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 // thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 // thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 // thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 // thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 // thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 // thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 // thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 // thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1 // thd1 thd1 thd1 thd1
thd2가thd1보다 더 많이 실행되는 경향을 보임thd1이yield()를 호출할 때마다 CPU를thd2에게 양보하기 때문
-
join()로 제어하기1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
class MyThread implements Runnable { public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { System.out.print(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " "); Thread.yield(); // 예제 5와 동일하게 yield 사용 } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
public class Main { public static void main(String args[]) throws InterruptedException { Thread my_thread1 = new Thread(new MyThread(), "thd1"); Thread my_thread2 = new Thread(new MyThread(), "thd2"); my_thread1.start(); my_thread2.start(); my_thread1.join(); // my_thread1이 종료될 때까지 main 스레드 대기 System.out.println("main thread"); } } // thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 // thd1 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd1 thd2 thd2 // thd1 thd1 thd2 thd2 thd1 thd1 thd2 // thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 // thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 // thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 // thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 // thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 // thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 // thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 // thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 // thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 // thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 // ... ... // thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 // thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 // thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 // thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 // thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 // thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 // thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 // thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 // thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 // thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 thd2 thd1 // thd2 thd1 thd2 thd2 main thread
thd1과thd2가 번갈아 실행되다가,thd1이 종료된 후main thread가 출력 됨- 이는
my_thread1.join()호출 때문에main스레드가my_thread1의 종료를 기다리기 때문
-
interrupt()로 제어하기1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
class MyThread extends Thread { Thread thdNext = null; // 다음 스레드를 저장할 변수 String szName; public MyThread(String szName) { super(szName); this.szName = szName; } public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(1000000); // 매우 긴 시간 sleep } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.print(getName() + " "); // 인터럽트 발생 시 스레드 이름 출력 if (thdNext.isAlive()) { // 다음 스레드가 살아있으면 thdNext.interrupt(); // 다음 스레드 인터럽트 } } } } public void setNextThread(Thread t) { thdNext = t; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
public class Main { public static void main(String args[]) { MyThread my_thread1 = new MyThread("thd1"); MyThread my_thread2 = new MyThread("thd2"); MyThread my_thread3 = new MyThread("thd3"); my_thread1.setNextThread(my_thread2); // thd1 다음에 thd2 my_thread2.setNextThread(my_thread3); // thd2 다음에 thd3 my_thread3.setNextThread(my_thread1); // thd3 다음에 thd1 (순환) my_thread1.start(); my_thread2.start(); my_thread3.start(); try { my_thread1.interrupt(); // my_thread1을 인터럽트 my_thread2.join(); // my_thread2 종료 대기 my_thread3.join(); // my_thread3 종료 대기 } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println(e); } System.out.println("main"); } } // thd1 thd2 thd3 thd1 thd2 thd3 thd1 thd2 thd3 // thd1 thd2 thd3 thd1 thd2 thd3 thd1 thd2 thd3 // ... ... // thd1 thd2 thd3 main
my_thread1.interrupt()가 호출되면my_thread1은sleep()상태에서 깨어나InterruptedException을 catch 함catch블록에서thd1을 출력하고thdNext가 살아있으면my_thread2를 인터럽트 함- 이 과정이
thd2,thd3로 연쇄적으로 이어지면서 각 스레드가InterruptedException을 처리하고 종료 됨 - 마지막으로
my_thread2.join()과my_thread3.join()에 의해main스레드는 이들 스레드가 종료될 때까지 기다린 후main을 출력하고 종료 됨
스레드 동기화
스레드 간섭
-
여러 개의 스레드들이 하나의 공유 객체에 동시 접근하는 경우 데이터 무결성이 깨짐
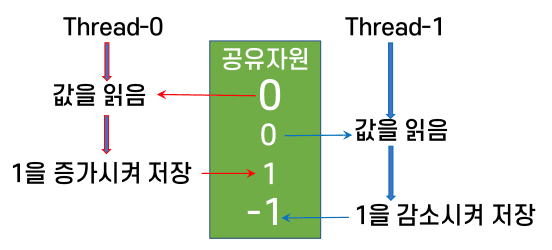
스레드 간섭 예
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
class Counter {
// 카운터 값을 저장하는 변수, 초기값은 0
private int c = 0;
// c 값을 1 증가
public void increment() {
c++;
}
// c 값을 1 감소
public void decrement() {
c--;
}
// 현재 c 값을 반환
public int value() {
return c;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
class MyThread1 implements Runnable {
Counter c;
public MyThread1(Counter c) {
this.c = c;
}
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
c.increment();
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
class MyThread2 implements Runnable {
Counter c;
public MyThread2(Counter c) {
this.c = c;
}
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
c.decrement();
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) throws InterruptedException {
// 공유될 Counter 객체 생성
Counter c = new Counter();
// 값을 증가시키는 CounterMyThread1 스레드 생성
Thread t1 = new Thread(new CounterMyThread1(c));
// 값을 감소시키는 CounterMyThread2 스레드 생성
Thread t2 = new Thread(new CounterMyThread2(c));
// 두 스레드를 시작
t1.start();
t2.start();
// 두 스레드가 작업을 종료할 때까지 대기
t1.join();
t2.join();
// Counter 객체의 최종 값을 출력
System.out.println(c.value());
}
}
- 동기화가 제대로 이루어지지 않은 상태에서 출력 된 값은 실행할 때마다 달라질 수 있음
스레드 동기화
- 서로 다른 스레드들이 공유 자원을 다룰 때, 데이터 무결성을 보장하도록 하는 것
- 한 번에 오직 한 개의 스레드만이 해당 공유 객체에 접근하도록 동기화 함(상호 배제)
- 동기화 방법
- 상호 배제 원칙
- 키워드
synchronized- 동기화 메서드 또는 동기화 블록을 제공
- 공유 자원을 수정할 때, 다른 스레드에서 같은 코드를 수행할 수 없게 함(잠금 설정)
synchronized메서드
synchronized는 스레드 동기화를 위한 키워드- 한번에 하나의 스레드에 의해서만 실행 가능하게 함
synchronized메서드를 실행하려면 메서드를 호출한 객체에 대한 lock을 얻어야 함- 다른 스레드는 잠금이 해제되고 lock을 얻을 때까지 동일 객체의
synchronized메서드를 실행할 수 없고 대기해야 함
1 2 3
public synchronized void func() { }
- 다른 스레드는 잠금이 해제되고 lock을 얻을 때까지 동일 객체의
-
일부 블록만 동기화하는 것도 가능함
1 2 3
synchronized(객체) { }
- 객체는 공유 자원으로 대개
this를 사용
- 객체는 공유 자원으로 대개
synchronized 메서드 사용 예
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
class Counter {
private int c = 0;
public synchronized void increment() { c++; }
public synchronized void decrement() { c--; }
public int value() { return c; }
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
class Counter {
private int c = 0;
public void increment() {
synchronized(this) { c++; }
}
public void decrement() {
synchronized(this) { c--; }
}
public int value() { return c; }
}
학습 정리
- 멀티 스레드 프로그래밍이란 하나의 프로세스에서 여러 스레드가 생성 되어 동시 실행되게 하는 것을 말함
- 스레드의 실행 코드는 스레드 생성에 사용 되는
Thread를 상속 받는 클래스나Runnable인터페이스를 구현한 클래스에서 정의 되어 있는public void run()메소드임 - 스레드는 생성 되어 소멸할 때까지 Startable, Runnable, Running, Not Running 등의 상태를 거침
Thread클래스에서 스레드의 상태를 제어하는 메소드로start(),join(),interrupt()가 있으며,static메소드인yield()와sleep()도 있음- 스레드 동기화는 데이터의 무결성을 유지하도록 한번에 한 스레드만이 스레드 간 공유 객체에 접근하도록 하는 것이며,
synchronized메소드는 동기화를 보장함
연습 문제
-
스레드 동기화와 관련 된 다음 설명 중 올바른 것은?
a. 메소드
notify()는 현재 실행 중인 스레드를 정해진 시간 동안 중지 시킨다. -
스레드 동기화의 의미를 가장 잘 설명한 것은?
a. 한 순간에 한 스레드만 공유 객체에 접근할 수 있게 하는 것
-
밑줄 부분에 들어갈 스레드 동기화를 위한 자바 키워드는 무엇인가?
1
여러 스레드가 공유 객체를 사용할 때, 한 스레드가 공유 객체의 ______ 메소드를 실행 중이라면 다른 스레드가 동일 객체에 접근할 수 없다.
a.
synchronized