데이터 접근 기술 - 시작
- 김영한님의 스프링 DB 2편 강의를 통해 데이터 접근 기술의 종류와 특징, 그리고 프로젝트 구조에 대해 정리함
데이터 접근 기술
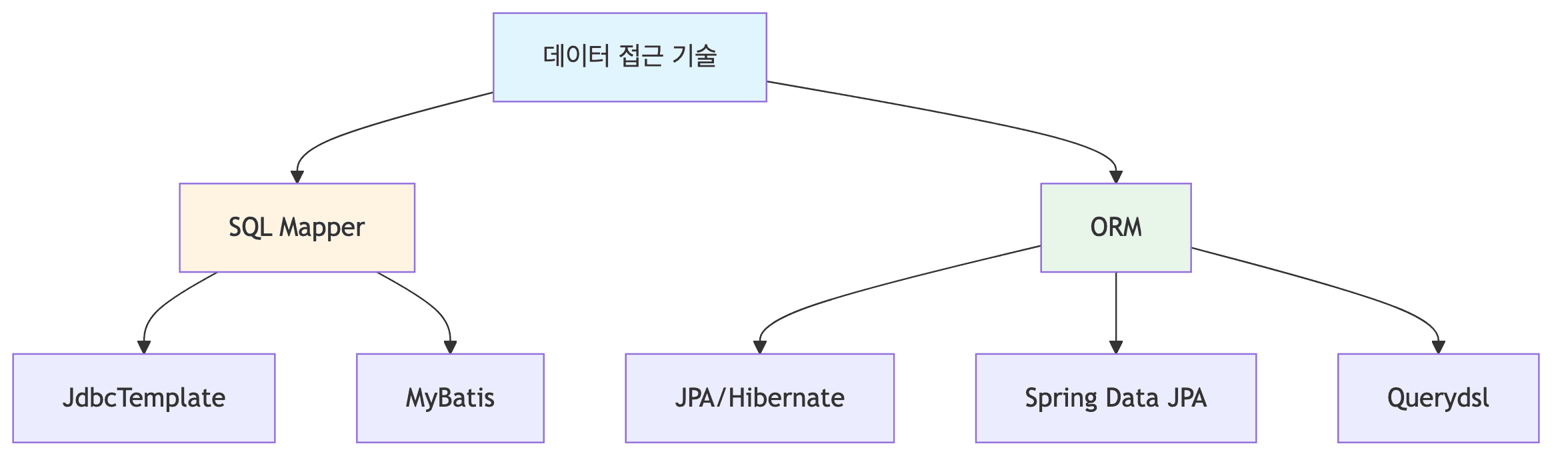
SQL Mapper
| 기술 | 특징 | 장점 | 단점 |
|---|---|---|---|
| JdbcTemplate | 스프링 내장 | 설정 간단, 빠른 학습 | SQL 직접 작성 |
| MyBatis | XML/어노테이션 매핑 | 복잡한 쿼리 작성 용이 | 설정 필요 |
- 개발자가 SQL을 직접 작성함
- JDBC의 반복 코드를 제거해줌
- 결과를 객체로 자동 매핑해줌
ORM
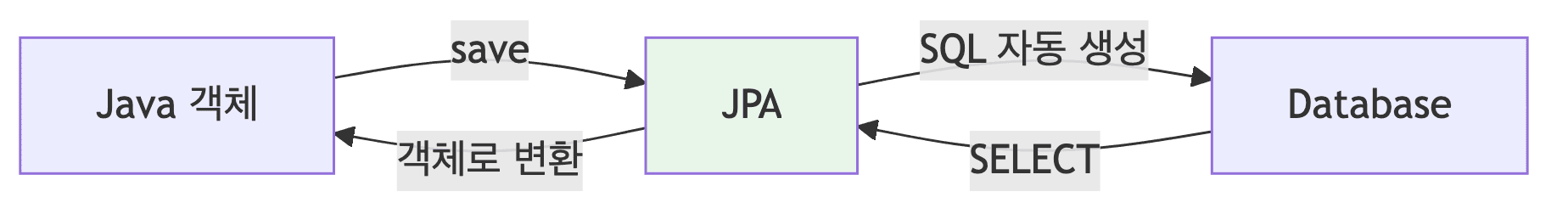
- 데이터베이스 테이블과 객체를 매핑함
- 개발자가 SQL을 직접 작성하지 않아도 JPA가 자동으로 SQL을 생성하고 실행함
- 데이터베이스 벤더가 변경되어도 코드를 수정할 필요가 거의 없음
- JPA (Java Persistence API)
- 자바의 ORM 표준 인터페이스
- Hibernate
- JPA 인터페이스의 대표적인 구현체
- 실제 내부 동작을 담당함
- Spring Data JPA
- JPA를 더욱 편리하게 사용할 수 있도록 도와주는 스프링 프레임워크의 모듈
- Querydsl
- 복잡한 동적 쿼리나 조인 등을 자바 코드로 안전하게 작성할 수 있게 도와주는 프레임워크
프로젝트 구조 - 도메인과 리포지토리
전체 아키텍처
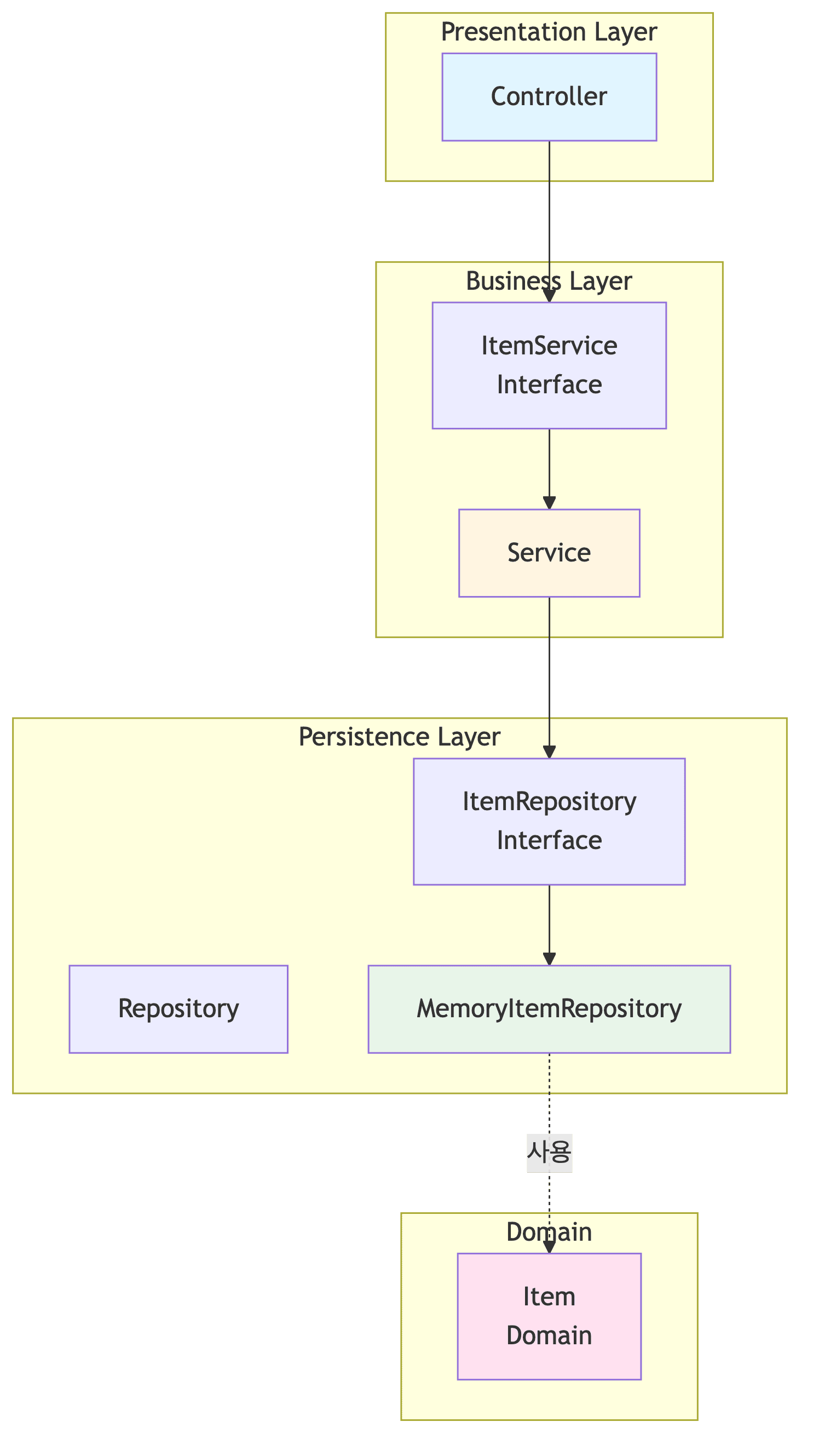
도메인 모델
-
Item 엔티티
-
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
@Data public class Item { private Long id; private String itemName; private Integer price; private Integer quantity; public Item() {} // JPA 등 프레임워크 사용 시 필수 public Item(String itemName, Integer price, Integer quantity) { this.itemName = itemName; this.price = price; this.quantity = quantity; } }
id는 생성자에서 제외함 (DB가 자동 생성)Integer를 사용함 (null 허용을 위해)- 기본 생성자가 필수임 (JPA, 프레임워크 호환)
DTO 설계
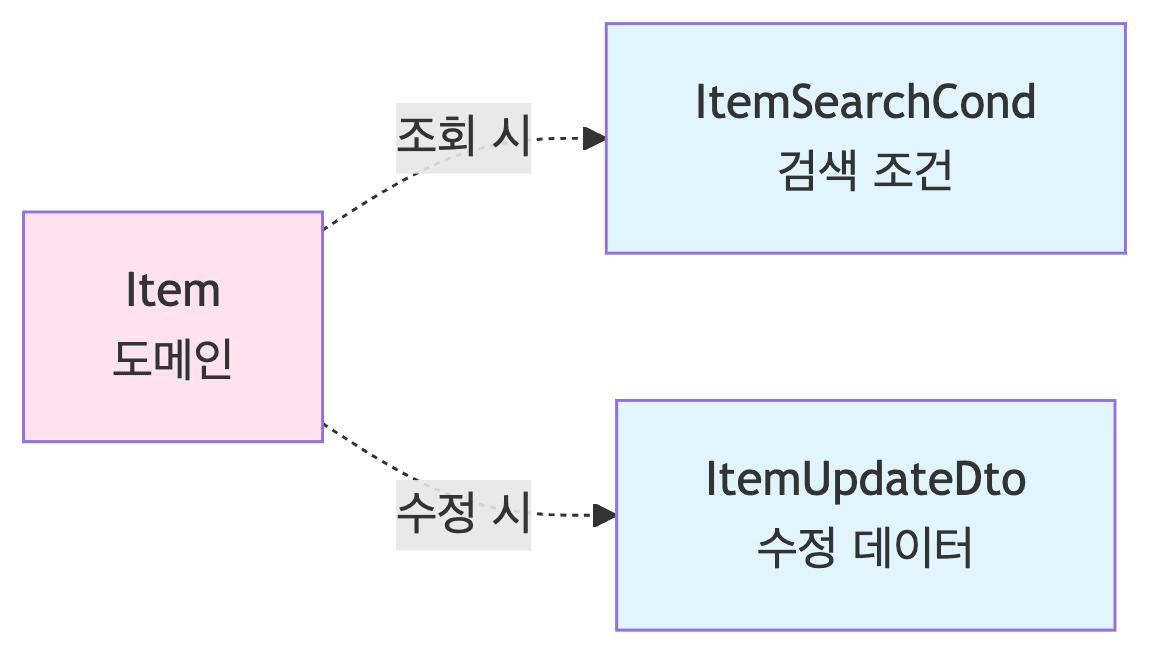
-
ItemSearchCond (검색 조건)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
@Data public class ItemSearchCond { private String itemName; // 검색어 private Integer maxPrice; // 최대 가격 public ItemSearchCond() {} public ItemSearchCond(String itemName, Integer maxPrice) { this.itemName = itemName; this.maxPrice = maxPrice; } }
-
ItemUpdateDto (수정 데이터)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
@Data public class ItemUpdateDto { private String itemName; private Integer price; private Integer quantity; // id는 제외 (URL 경로로 넘어오므로 DTO에 불필요) }
- DTO 사용 이유
- 명확한 의도 표현
- 수정용 객체인지 조회용 객체인지 이름만으로 명확하게 알 수 있음 (
ItemUpdateDto)
- 수정용 객체인지 조회용 객체인지 이름만으로 명확하게 알 수 있음 (
- 불필요한 데이터 노출 방지
id처럼 수정하면 안 되거나 필요 없는 데이터를 제외하여 안전성을 높임
- 도메인 모델 보호
- 도메인 객체를 그대로 사용하면 화면이나 API 요구사항에 따라 도메인 로직이 변경될 위험이 있음
- 명확한 의도 표현
- DTO 사용 이유
리포지토리 인터페이스
-
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
public interface ItemRepository { Item save(Item item); void update(Long itemId, ItemUpdateDto updateParam); Optional<Item> findById(Long id); List<Item> findAll(ItemSearchCond cond); }
-
인터페이스 도입 이유
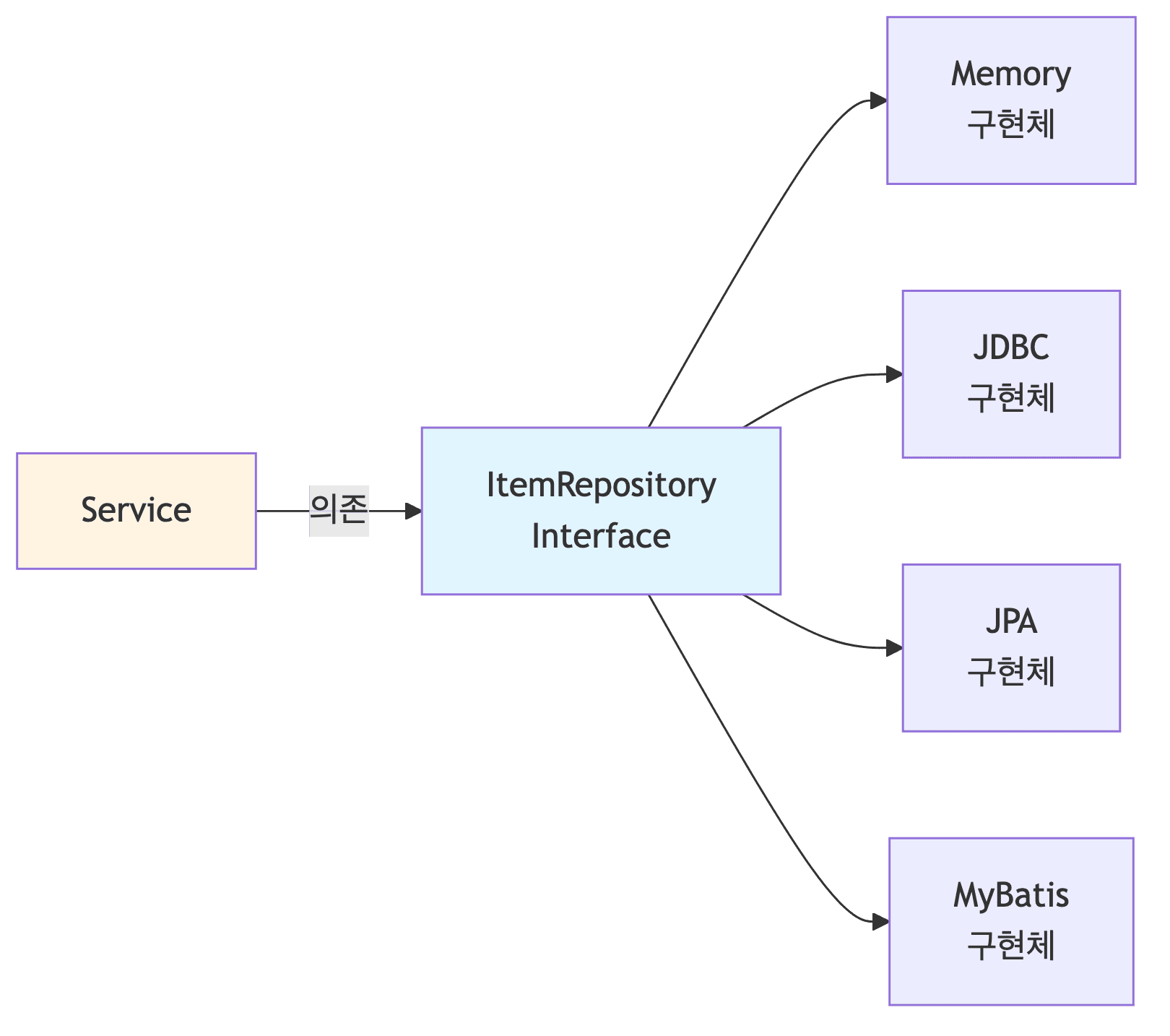
- 장점
- 구현 기술 변경이 용이함
- 테스트 시 Mock 사용이 가능함
- OCP 원칙을 준수할 수 있음
- 장점
메모리 리포지토리 구현
-
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47
@Repository public class MemoryItemRepository implements ItemRepository { private static final Map<Long, Item> store = new HashMap<>(); // 메모리 저장소 private static long sequence = 0L; @Override public Item save(Item item) { item.setId(++sequence); store.put(item.getId(), item); return item; } @Override public void update(Long itemId, ItemUpdateDto updateParam) { Item findItem = findById(itemId).orElseThrow(); findItem.setItemName(updateParam.getItemName()); findItem.setPrice(updateParam.getPrice()); findItem.setQuantity(updateParam.getQuantity()); } @Override public Optional<Item> findById(Long id) { return Optional.ofNullable(store.get(id)); } @Override public List<Item> findAll(ItemSearchCond cond) { String itemName = cond.getItemName(); Integer maxPrice = cond.getMaxPrice(); // 자바 스트림으로 필터링 구현 return store.values().stream() .filter(item -> { if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(itemName)) return true; return item.getItemName().contains(itemName); // 부분 일치 }) .filter(item -> { if (maxPrice == null) return true; return item.getPrice() <= maxPrice; // 가격 제한 }) .collect(Collectors.toList()); } public void clearStore() { store.clear(); // 테스트 격리를 위한 메서드 } }
-
검색 로직 흐름
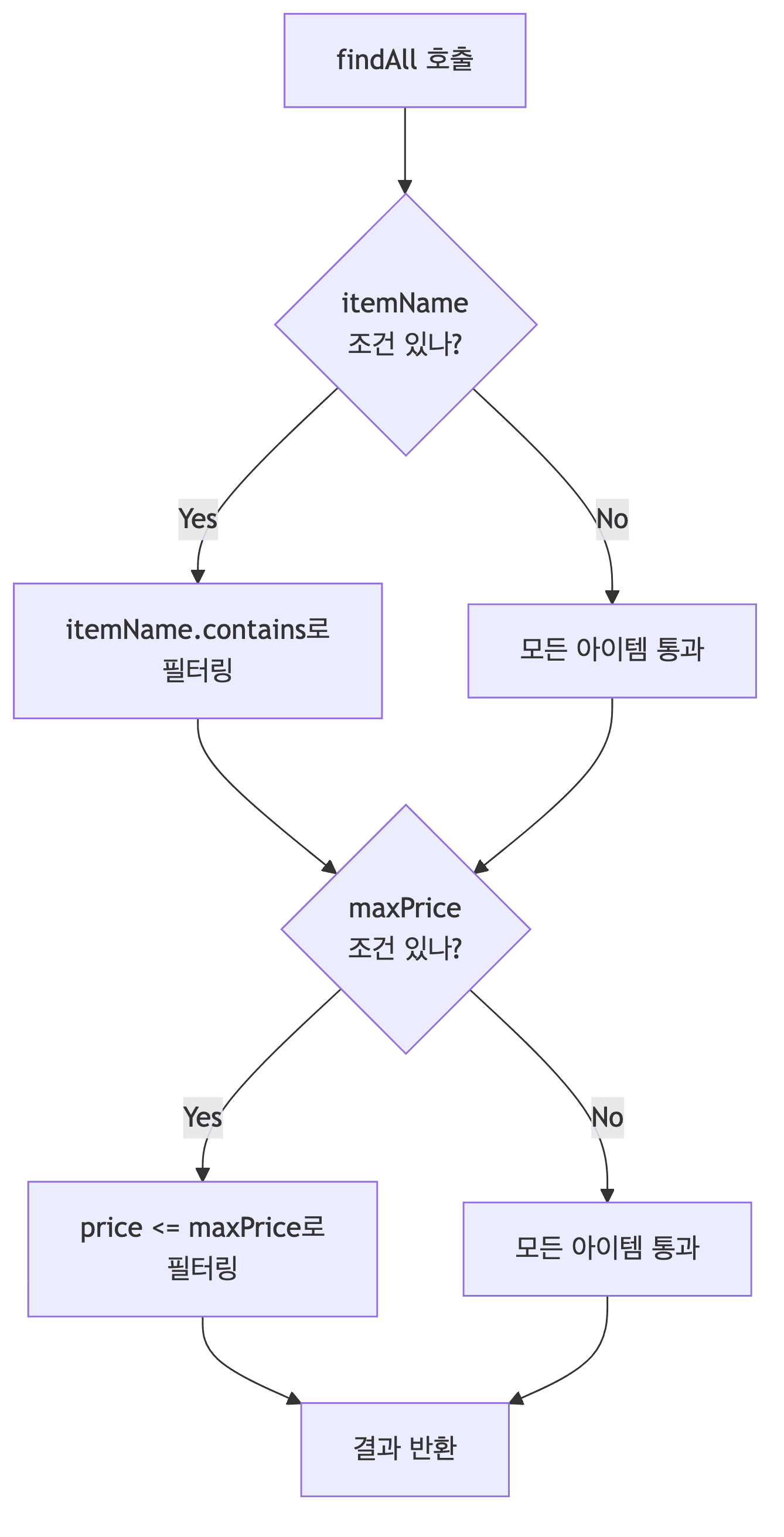
프로젝트 구조 - 서비스와 컨트롤러
서비스 계층
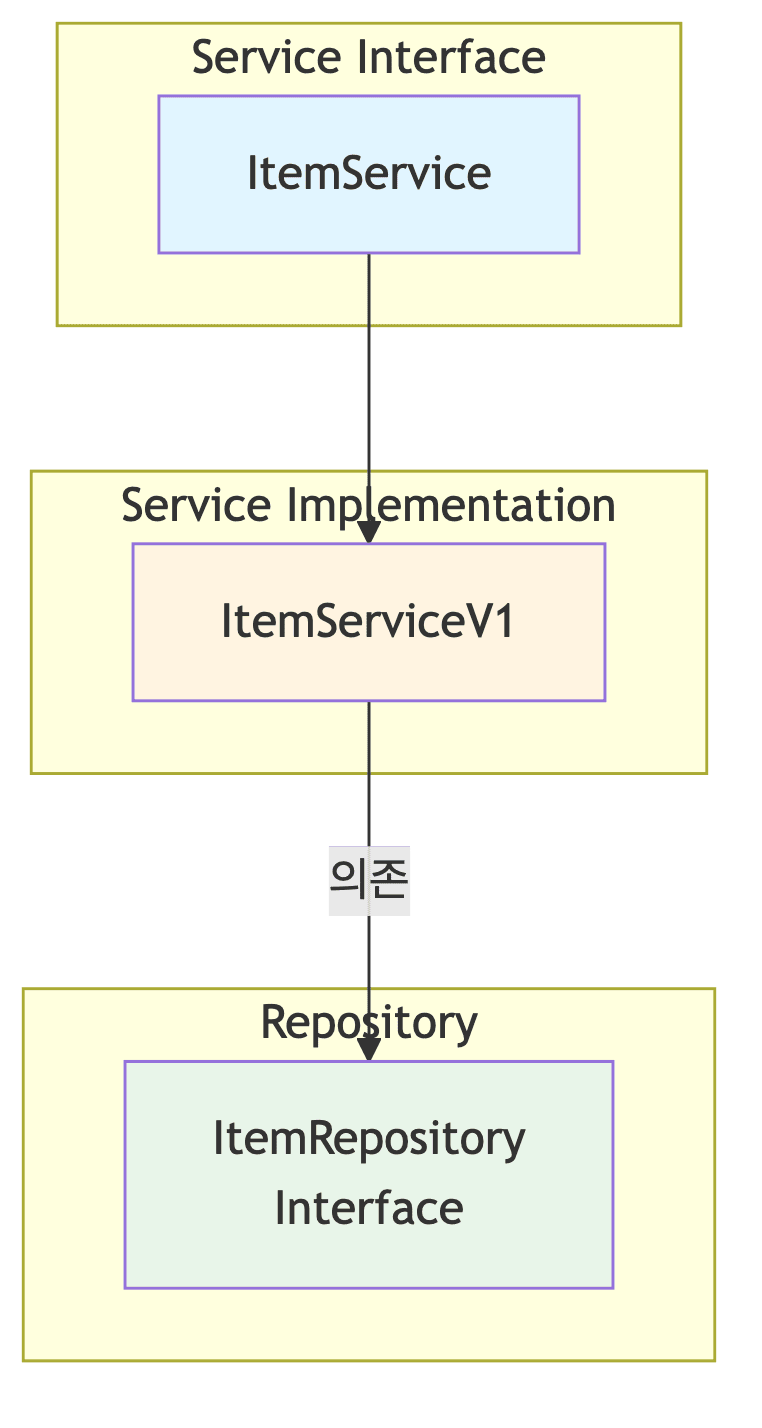
-
ItemService 인터페이스
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
public interface ItemService { Item save(Item item); void update(Long itemId, ItemUpdateDto updateParam); Optional<Item> findById(Long id); List<Item> findItems(ItemSearchCond itemSearch); }
-
ItemServiceV1 구현체
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
@Service @RequiredArgsConstructor // final 필드 생성자 자동 생성 public class ItemServiceV1 implements ItemService { private final ItemRepository itemRepository; @Override public Item save(Item item) { return itemRepository.save(item); // 리포지토리에 위임 } @Override public void update(Long itemId, ItemUpdateDto updateParam) { itemRepository.update(itemId, updateParam); } @Override public Optional<Item> findById(Long id) { return itemRepository.findById(id); } @Override public List<Item> findItems(ItemSearchCond cond) { return itemRepository.findAll(cond); } }
- 대부분의 로직을 리포지토리에 위임함
컨트롤러 계층
-
주요 엔드포인트
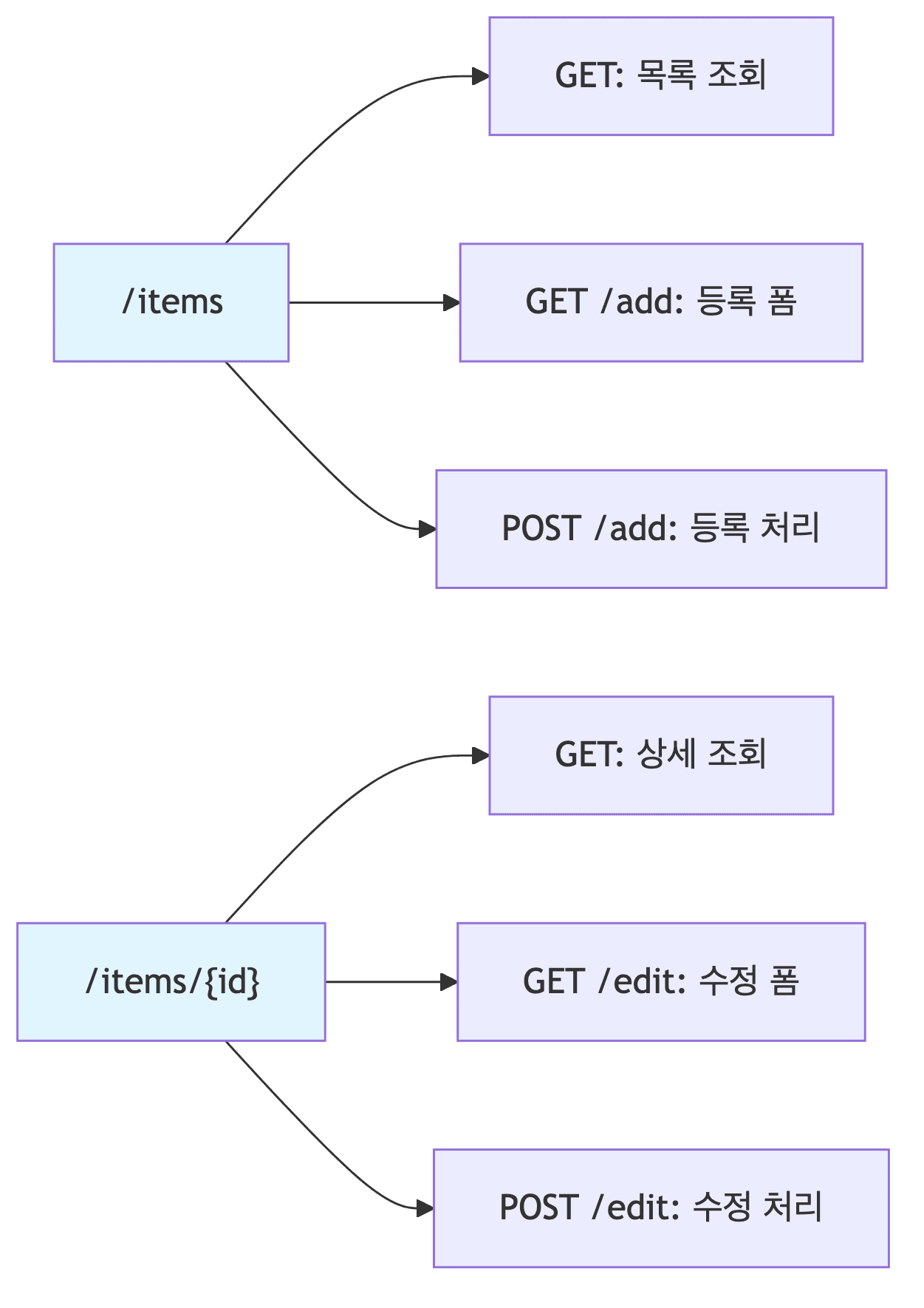
-
ItemController
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34
@Controller @RequestMapping("/items") @RequiredArgsConstructor public class ItemController { private final ItemService itemService; @GetMapping public String items(@ModelAttribute("itemSearch") ItemSearchCond itemSearch, Model model) { List<Item> items = itemService.findItems(itemSearch); model.addAttribute("items", items); return "items"; // 뷰 템플릿 반환 } @GetMapping("/{itemId}") public String item(@PathVariable long itemId, Model model) { Item item = itemService.findById(itemId).get(); model.addAttribute("item", item); return "item"; } @PostMapping("/add") public String addItem(@ModelAttribute Item item, RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes) { Item savedItem = itemService.save(item); redirectAttributes.addAttribute("itemId", savedItem.getId()); redirectAttributes.addAttribute("status", true); // 쿼리 파라미터로 전달됨 return "redirect:/items/{itemId}"; // PRG 패턴 적용 } @PostMapping("/{itemId}/edit") public String edit(@PathVariable Long itemId, @ModelAttribute ItemUpdateDto updateParam) { itemService.update(itemId, updateParam); return "redirect:/items/{itemId}"; } }
-
PRG 패턴 (Post-Redirect-Get)
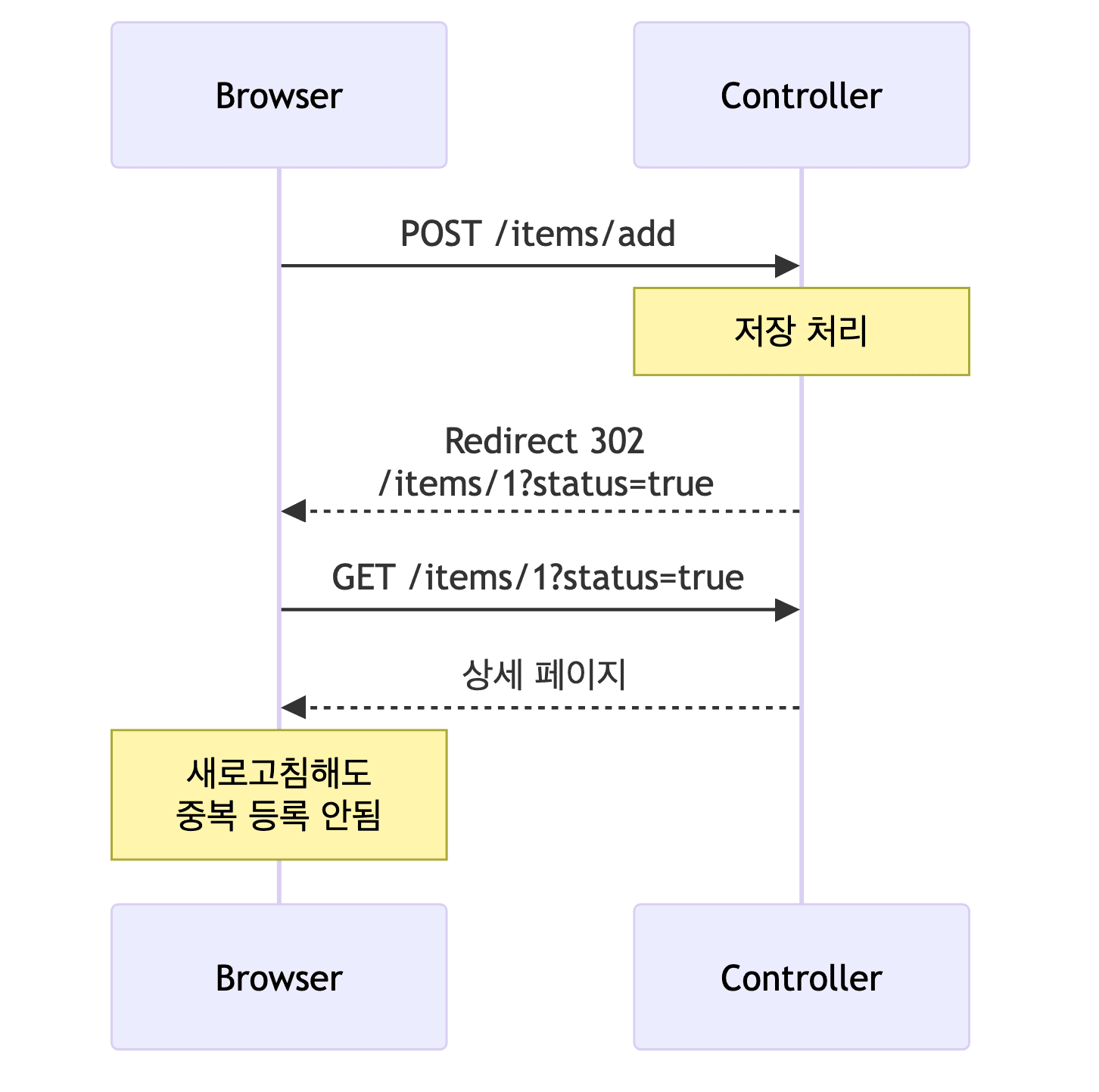
-
프로젝트 설정
의존성 구성
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
dependencies {
// 웹 & 뷰
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
// 유틸리티
compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
annotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
// 테스트
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
testCompileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
testAnnotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
}
스프링 빈 설정
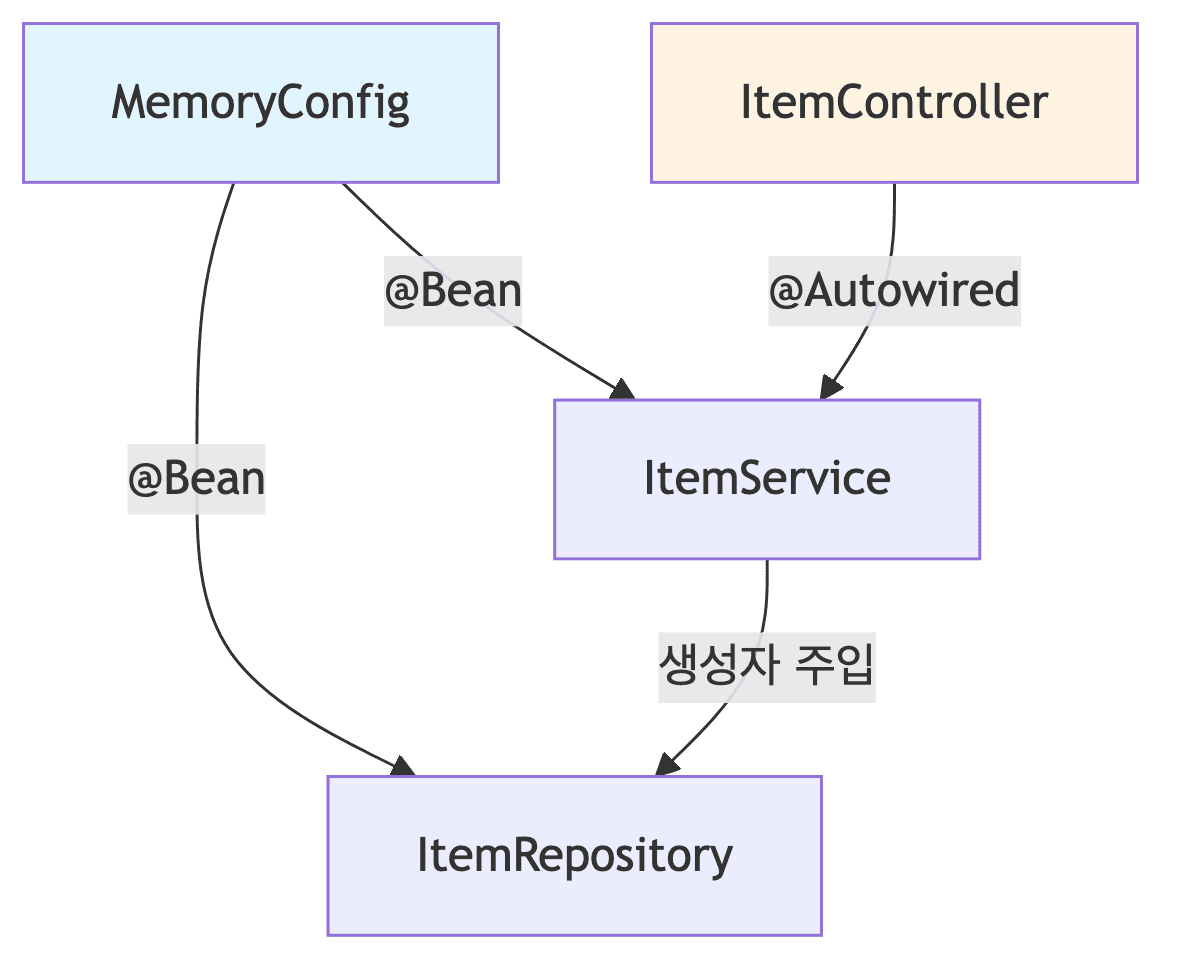
-
MemoryConfig
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
@Configuration public class MemoryConfig { @Bean // 빈 직접 등록 public ItemService itemService() { return new ItemServiceV1(itemRepository()); } @Bean public ItemRepository itemRepository() { return new MemoryItemRepository(); // 추후 구현체 교체의 유연성을 위해 수동 등록 } }
- 수동 빈 등록 이유
- 구현체를 쉽게 교체하기 위함임
- 컨트롤러는 컴포넌트 스캔을 사용함
- 수동 빈 등록 이유
-
메인 애플리케이션
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
@Import(MemoryConfig.class) // 설정 파일 추가 @SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages = "hello.itemservice.web") // 컴포넌트 스캔 범위 지정 public class ItemServiceApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ItemServiceApplication.class, args); } @Bean @Profile("local") // local 프로필에서만 이 빈을 등록 public TestDataInit testDataInit(ItemRepository itemRepository) { return new TestDataInit(itemRepository); } }
프로필 설정
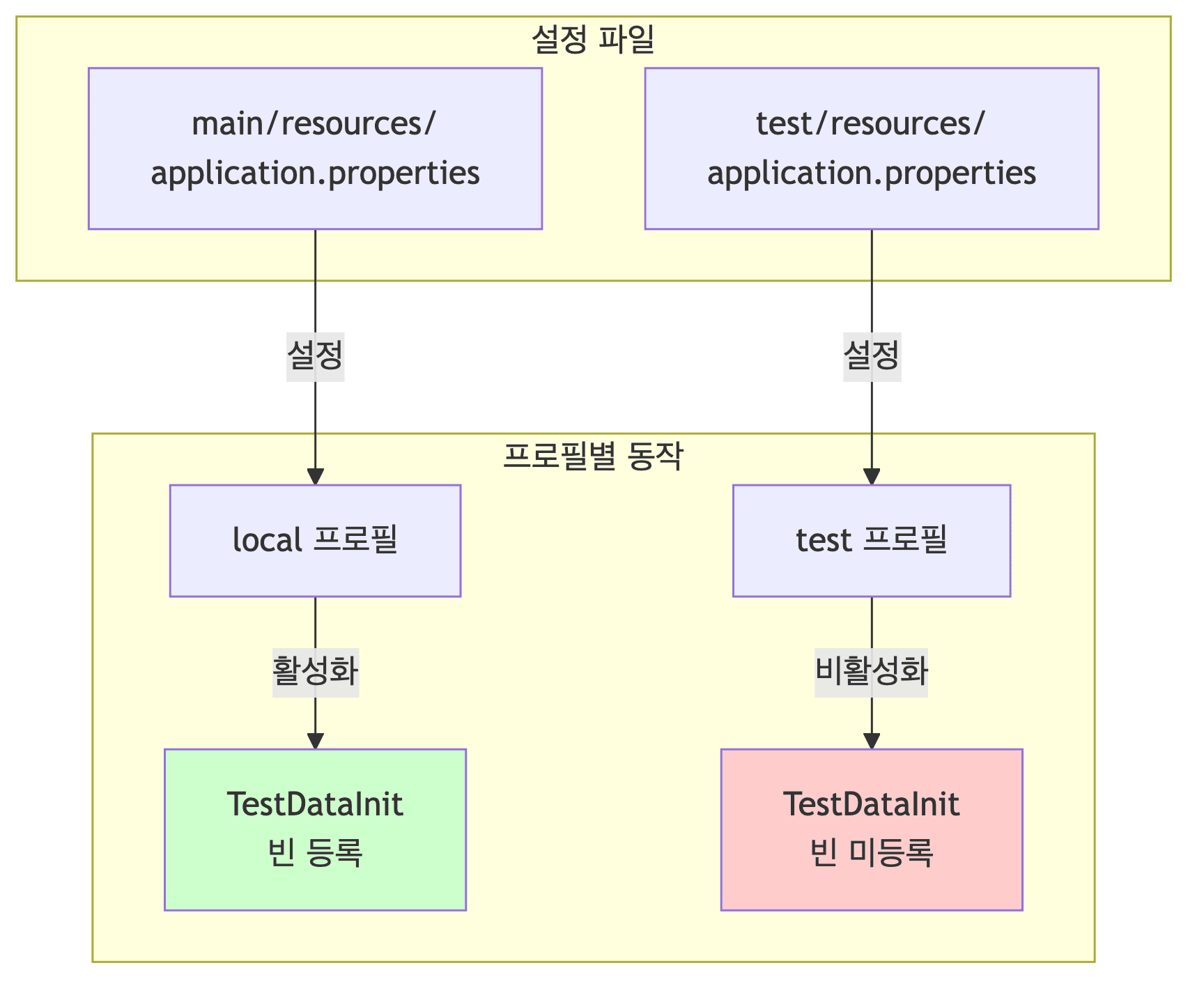
-
main 프로필 (로컬 실행)
- src/main/resources/application.properties
1
spring.profiles.active=local
- 결과
@Profile("local")이 활성화됨TestDataInit빈이 등록됨- 초기 데이터가 자동 생성됨
-
test 프로필 (테스트 실행)
- src/test/resources/application.properties
1
spring.profiles.active=test
- 결과
@Profile("local")이 비활성화됨TestDataInit빈이 등록되지 않음- 깨끗한 상태로 테스트가 가능함
-
TestDataInit
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
@Slf4j @RequiredArgsConstructor public class TestDataInit { private final ItemRepository itemRepository; /** * 확인용 초기 데이터 추가 */ @EventListener(ApplicationReadyEvent.class) // 스프링 컨테이너 준비 완료 후 실행 public void initData() { log.info("test data init"); itemRepository.save(new Item("itemA", 10000, 10)); itemRepository.save(new Item("itemB", 20000, 20)); } }
-
이벤트 리스너 선택 이유
@PostConstruct의 문제점- 빈의 초기화 시점에는 AOP(예:
@Transactional)가 아직 적용되지 않을 수 있음 - 이로 인해 트랜잭션 등 AOP 기능이 필요한 로직 실행 시 문제가 발생할 수 있음
- 빈의 초기화 시점에는 AOP(예:
ApplicationReadyEvent의 장점- 스프링 컨테이너가 완전히 초기화된 후에 실행됨
- AOP를 포함한 모든 빈이 준비된 상태이므로 안전하게 로직을 수행할 수 있음
테스트 전략
테스트 원칙
- 독립성
- 서로 영향을 주지 않아야 함
- 순서와 무관하게 실행되어야 함
- 반복성
- 항상 같은 결과를 보장해야 함
- 실행 환경에 독립적이어야 함
- 격리성
- 테스트 실행 전후로 데이터 초기화가 필요함
- 트랜잭션 롤백 등을 통해 상태를 격리해야 함
ItemRepositoryTest
-
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
@SpringBootTest // 통합 테스트 class ItemRepositoryTest { @Autowired ItemRepository itemRepository; @AfterEach // 각 테스트 종료 후 실행 void afterEach() { // 메모리 저장소인 경우만 초기화 (테스트 격리) if (itemRepository instanceof MemoryItemRepository) { ((MemoryItemRepository) itemRepository).clearStore(); } } @Test void save() { // given Item item = new Item("itemA", 10000, 10); // when Item savedItem = itemRepository.save(item); // then Item findItem = itemRepository.findById(item.getId()).get(); assertThat(findItem).isEqualTo(savedItem); // 저장된 데이터 검증 } // ... update, findItems 테스트 생략 }
연습 문제
-
데이터 접근 기술 분류 중 SQL Mappers와 ORM의 주된 차이는 무엇일까요?
a. SQL Mappers는 SQL 결과와 객체를 매핑합니다.
- SQL Mappers는 개발자가 작성한 SQL의 결과를 객체로 매핑하는 반면, ORM은 기본적인 SQL을 자동으로 생성하여 JDBC 코드의 많은 부분을 줄여줌
- 둘 다 데이터와 객체 연동 방식에서 차이가 있음
-
프로젝트에서 DTO(Data Transfer Object)의 주된 목적은 무엇인가요?
a. 데이터를 효율적으로 전달하기 위해서
DTO는 주로 계층 간(예: 컨트롤러-서비스, 서비스-리포지토리) 필요한 데이터를 묶어서 전달하는 데 사용되는 객체임- 데이터 자체를 운반하는 역할에 집중하며 로직은 최소화함
-
Spring Profiles는 주로 어떤 용도로 사용되나요?
a. 환경별로 다른 설정을 적용하기 위해서
Spring Profiles는 개발, 테스트, 운영 등 애플리케이션 실행 환경에 따라 데이터 소스 설정이나 특정 빈의 등록 여부 등 다양한 설정을 다르게 적용해야 할 때 유용하게 사용됨
-
JUnit 테스트에서
@AfterEach어노테이션이 붙은 메서드의 주된 역할은 무엇일까요?a. 각 테스트 케이스 실행 후 데이터를 정리합니다.
@AfterEach는 각 테스트 메서드가 실행될 때마다 그 직후에 호출되어 테스트 간 데이터 오염을 방지하고 독립적인 환경을 유지하는 역할을 함- 테스트 격리를 위해 중요함
-
데이터베이스 테이블의 주 식별자(Primary Key) 전략으로 권장되는 방식은 무엇인가요?
a. 시스템이 생성하는 임의의 대체 키
- 비즈니스적 의미를 갖는 자연 키는 변경될 위험이 있어 식별자로 불안정할 수 있음
- 시스템이 자동으로 생성하는 임의의 대체 키(예: 자동 증가 숫자)는 변경될 일이 없어 안정적인 주 식별자로 권장됨
요약 정리
- SQL Mapper(JdbcTemplate, MyBatis)는 SQL을 직접 작성하며 결과를 객체로 매핑해주는 반면, ORM(JPA, Querydsl)은 SQL을 자동 생성하여 객체 중심으로 개발할 수 있게 도와줌
- 도메인은 비즈니스 로직의 핵심이 되는 객체(엔티티)이며, 리포지토리는 이러한 도메인 객체를 저장하고 조회하는 데이터 접근 계층임
- 서비스 계층은 비즈니스 로직을 담당하며, 리포지토리 인터페이스에 의존하여 특정 데이터 접근 기술에 종속되지 않도록 설계하는 것이 중요함
- 컨트롤러는 웹 요청을 받아 서비스를 호출하고 그 결과를 반환하는 역할을 수행함
- 스프링 프로필(Profiles) 기능을 활용하면 로컬, 테스트, 운영 등 실행 환경에 따라 데이터베이스 연결 정보나 빈 설정을 유연하게 분리하여 관리할 수 있음
@Configuration과@Bean을 사용한 데이터 소스 및 빈 수동 등록은 향후 구현 기술 변경 시 코드를 최소한으로 수정할 수 있게 해주는 유연성을 제공함- 테스트 격리는 신뢰할 수 있는 테스트 환경을 위해 필수적이며,
@AfterEach등을 사용하여 각 테스트 실행 후 데이터를 초기화하거나 트랜잭션을 롤백하는 전략을 사용해야 함