학습 개요
- 파이썬은 객체 지향 프로그래밍 언어로 문법이 쉽고, 확장성이 좋아 데이터 과학 분야와 R과 더불어 널리 이용되고 있는 프로그램 언어임
- 파이썬을 설치하는 방법, 파이썬 프로그래밍에 대하여 공부함
학습 목표
- 파이썬을 설치하는 방법을 이해할 수 있음
- Spyder 및 Jupyter Notebook을 사용할 줄 암
- 파이썬 언어를 사용할 수 있음
강의록
파이썬 소개
Python(파이썬) 소개
- Platform independent
- Windows, Unix, MacOS, …
- Easy to install, learn & use
- Easy syntax, ….
- Easily extensible with library packages
- 개발자
- Guido van Rossum (1956.1.31~) 네덜란드
Python 설치
Anaconda (아나콘다)
Path 설정하기
- Windows 시스템 → 제어판 → 시스템 및 보안 → 시스템 → 고급 시스템 설정 → 환경 변수 → 시스템 변수에서 Path 편집 → 새로 만들기
- 추가 경로
- C:\ProgramData\anaconda3\
- C:\ProgramData\anaconda3\Scripts
- C:\ProgramData\anaconda3\Library\bin
- 추가 경로
pip: Python 패키지를 설치하고 관리하는 프로그램
-
패키지 설치하기
1 2 3 4 5
pip install mglearn pip install graphviz pip install pydot pip install pydotplus pip install tensorflow
Spyder 실행
1
2
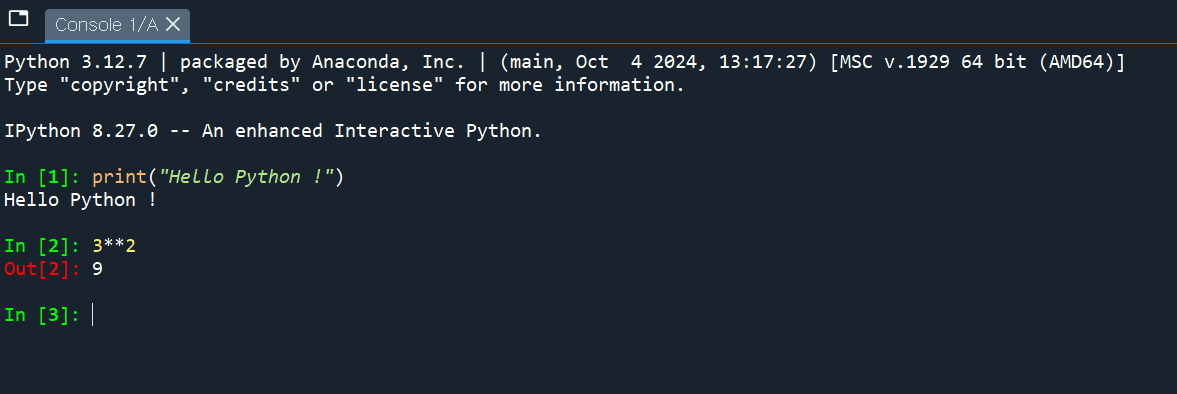
print("Hello Python !")
3**2
파이썬 프로그래밍
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
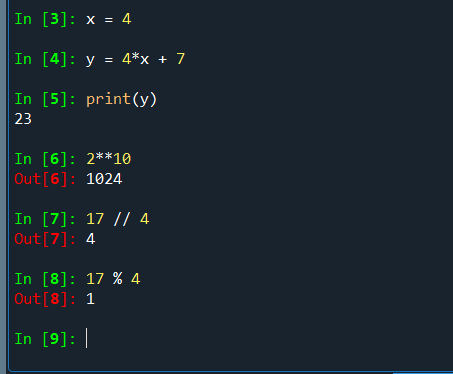
x = 4
y = 4 * x + 7
print(y)
2**10 # 1024
17 // 4 # 4
17 % 4 # 1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
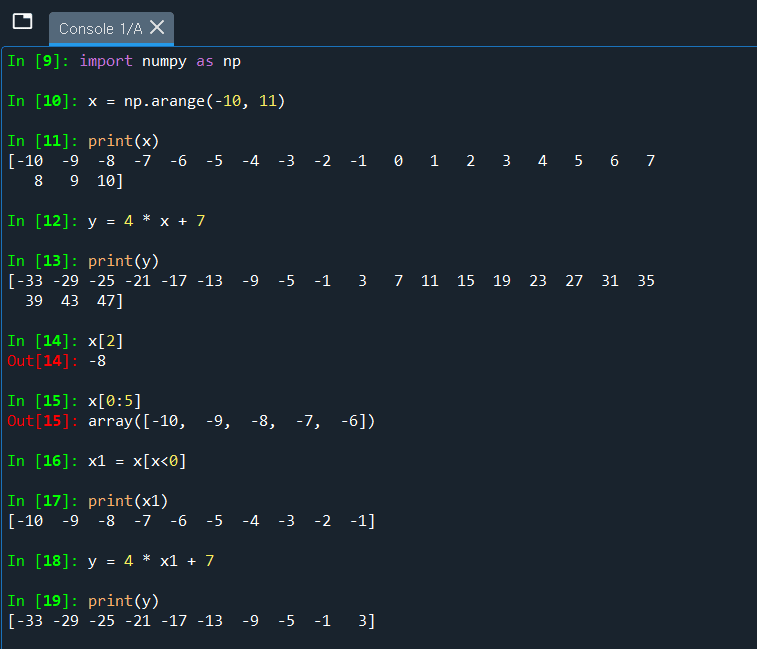
import numpy as np
x = np.arange(-10, 11)
print(x)
y = 4 * x + 7
print(y)
x[2]
x[0:5]
x1 = x[x<0]
print(x1)
y = 4 * x1 + 7
print(y)
Jupyter notebook 실행
- window 앱 검색
- Jupyter Notebook
-
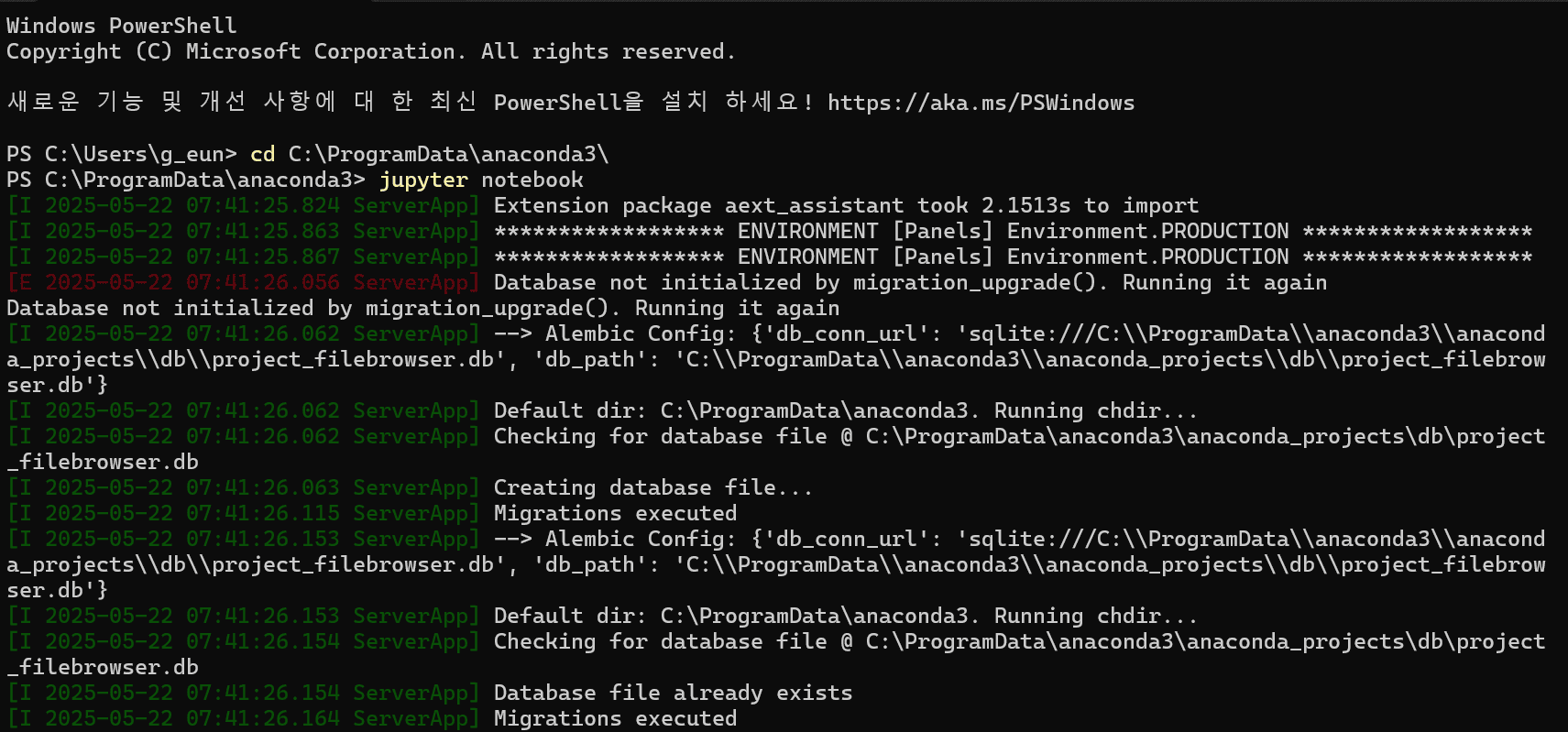
cmd 창에서 anaconda 설치 경로에서 jupyter notebook 명령어 입력
1
jupyter notebook
-
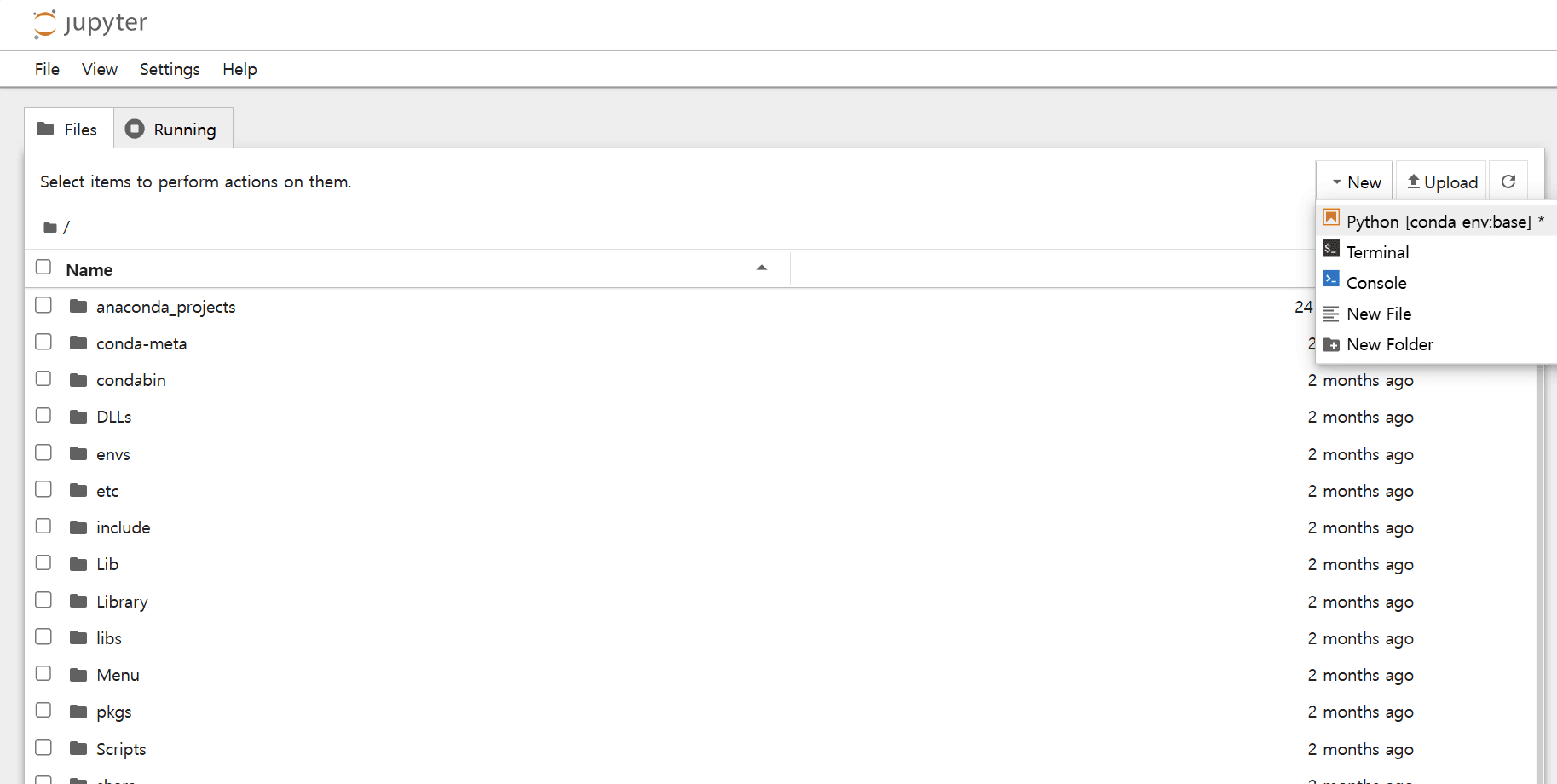
New - Python 3 선택
-
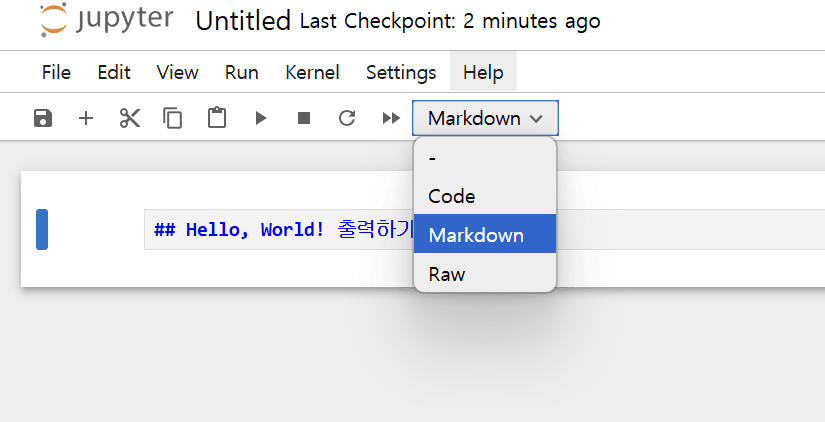
Markdown 선택 → 설명문 입력 → 실행
-
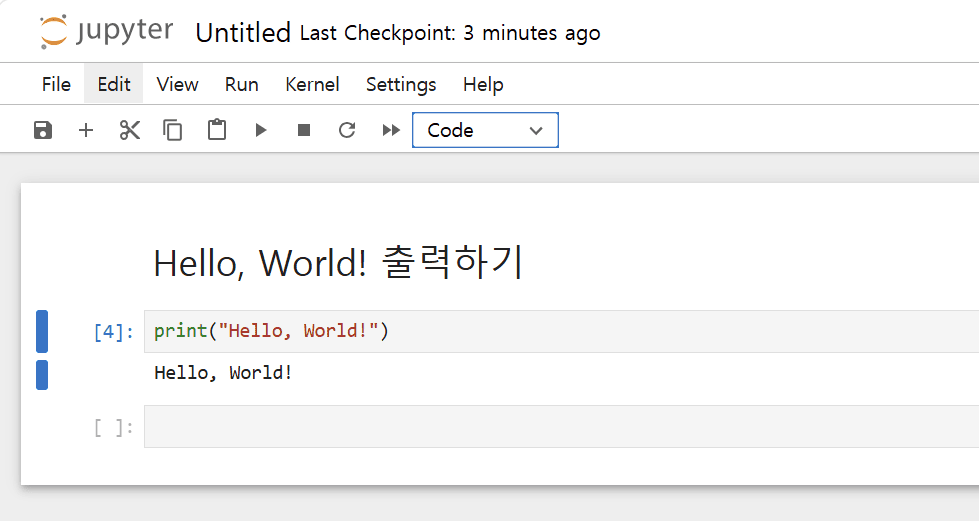
Code 선택 후 코드 입력 → 실행
1
print("Hello, World!")
Run python using Google Colab
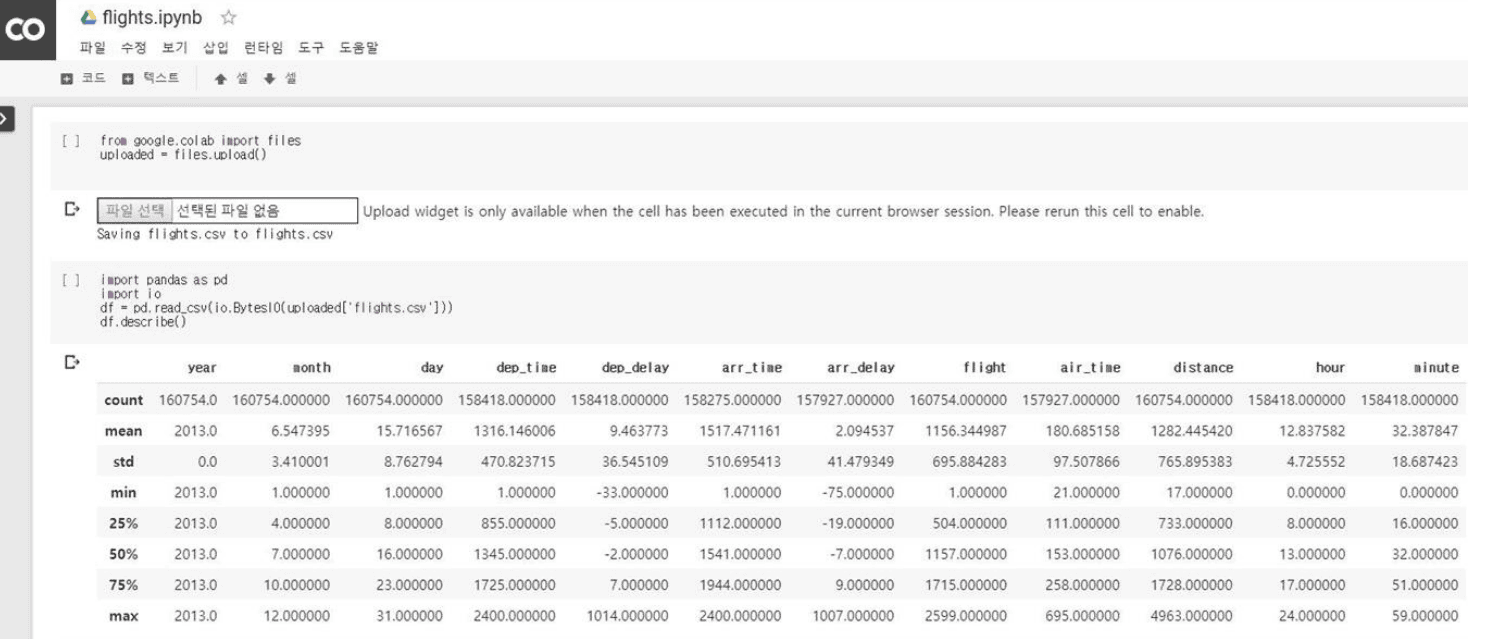
1
2
from google.colab import files
upload = files.upload()
1
2
3
4
import pandas as pd
import io
df = pd.read_csv(io.BytesIO(uploaded['filghts.csv']))
df.describe()
파이썬 프로그래밍
산술 연산
1
2
3
4
1 - 2 # 뺄셈
4 * 5 # 곱셈
7 / 5 # 나눗셈
3 ** 2 # 거듭 제곱
자료형
1
2
3
type(10) # int
type(2.710) # float
type("hello") # str
변수
1
2
3
4
5
x = 10
print(x)
y = 3.14
x * y
type(x * y) # float
리스트
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
a = [1,2,3,4,5]
print(a) # [1,2,3,4,5]
len(a) # 5
a[0] # 1
a[4] # 5
a[4] = 99
print(a) # [1,2,3,4,99]
a[0:2] # [1,2]
a[1:] # [2,3,4,99]
a[:3] # [1,2,3]
a[:-1] # [1,2,3,4]
a[:-2] # [1,2,3]
Dictionary : key 와 value 를 한 쌍으로 저장
1
2
3
4
5
me = {'height': 180, 'weight': 70}
me['height'] # 180
me['weight'] # 70
me['age'] = 30 # 새 원소 추가
print(me) # {'height': 180, 'weight': 70, 'age': 30}
-
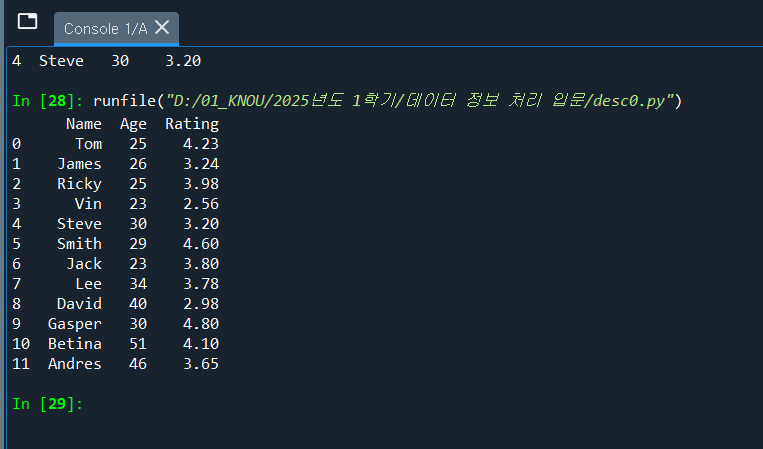
참고 : desc0.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
import pandas as pd import numpy as np #Create a Dictionary of series D = ({ 'Name' : pd.Series(['Tom','James','Ricky','Vin','Steve','Smith','Jack','Lee','David','Gasper','Betina','Andres']), 'Age' : pd.Series([25,26,25,23,30,29,23,34,40,30,51,46]), 'Rating' : pd.Series([4.23,3.24,3.98,2.56,3.20,4.6,3.8,3.78,2.98,4.80,4.10,3.65])}) #Create a DataFrame Df = pd.DataFrame(D) print(Df) Df.head()
1
runfile("D:/01_KNOU/2025년도 1학기/데이터 정보 처리 입문/desc0.py")
bool
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
hungry = True
sleepy = False
type(hungry) # bool
not hungry # False
hungry and sleepy # False
hungry or sleepy # True
if
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
hungry = True
if hungry:
print("I'm hungry")
# I'm hungry
hungry = False
if hungry:
print("I'm hungry")
else:
print("I'm not hungry")
print("I'm sleepy")
# I'm not hungry
# I'm sleepy
for : 반복문
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
for i in [1,2,3]:
print(i)
# 1
# 2
# 3
name = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
for i in name:
print(i)
# a
# b
# c
# d
# e
for : 반복문 - 계속
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
sum = 0
for i in range(10) :
sum = sum + i
print(sum)
# 45
# Note that range(10) is not the value of 0 to 10, but the values 0 to 9
함수
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
def hello():
print("Hello World !")
print("Welcome to Python class !")
hello()
# Hello World !
# Welcome to Python class !
def hello2(object):
print("Hello " + object + " !")
hello2("Jang")
# Hello Jang !
클래스
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
class Man:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
print("Initialized !")
def hello(self):
print("Hello " + self.name + " !")
def goodbye(self):
print("Good-bye " + self.name + " !")
m = Man("David")
# Initialized !
m.hello()
# Hello David !
m.goodbye()
# Good-bye David !
클래스 - 계속 1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
class Person:
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
def disp(self):
print(self.name)
print(self.age)
p1 = Person('홍길동', 22)
p2 = Person('철수', 35)
p1.disp()
# 홍길동
# 22
p2.disp()
# 철수
# 35
클래스 - 계속 2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
class Person2:
def __init__(self):
self.name = input('Name:')
self.age = int(input('Age:'))
def disp(self):
print('Name =',self.name)
print('Age =',self.age)
customer = []
for i in range(5):
customer.append(Person2())
# >>> customer[0].disp()
# Name:AAA
# Age:12
# >>> customer[1].disp()
# Name:BBB
# Age:25
# ...
Numpy 가져오기
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
import numpy as np
x = np.array([1.0, 2.0, 3.0])
print(x) # [1. 2. 3.]
type(x) # numpy.ndarray
y = x/3
print(y) # [0.33333333 0.66666667 1.]
x = np.array([1.0, 2.0, 3.0])
y = np.array([2.0, 4.0, 6.0])
x + y # array([3., 6., 9.])
x - y # array([-1., -2., 0.])
x * y # array([ 2., 8., 36.])
x / y # array([0.5, 0.5, 1. ])
Numpy - N차원 배열
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
import numpy as np
A = np.array([[5,7], [9,11]])
print(A)
# [[ 5 7]
# [ 9 11]]
A[0] # array([5, 7])
A[1] # array([ 9, 11])
A[0,0] # 5 - A[0][0]
A[1,0] # 9 - A[1][0]
B = np.array([[3,0], [0,6]])
A + B
# array([[ 8, 7], [ 9, 17]])
A * B
# array([[15, 0], [ 0, 66]])
Broadcast : 형상이 다른 배열 계산
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
import numpy as np
A = np.array([[1,2], [3,4]])
B = np.array([10,20])
C = 10
A * B
# array([[10, 40], [30, 80]])
A * C
# array([[10, 20], [30, 40]])
원소 접근 : 원소의 인덱스는 0부터 시작
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
X = np.array([[51,55], [14,19], [0,4]])
print(X)
# [[51 55]
# [14 19]
# [ 0 4]]
X[0] # array([51, 55])
X[0][1] # array([55])
X[0,1] # 55
Y = X.flatten()
print(Y)
# [51 55 14 19 0 4]
for row in X:
print(row)
# [51 55]
# [14 19]
# [0 4]
Y > 15
# array([True, True, False, True, False, False])
Y[Y > 15]
# array([51, 55, 19])
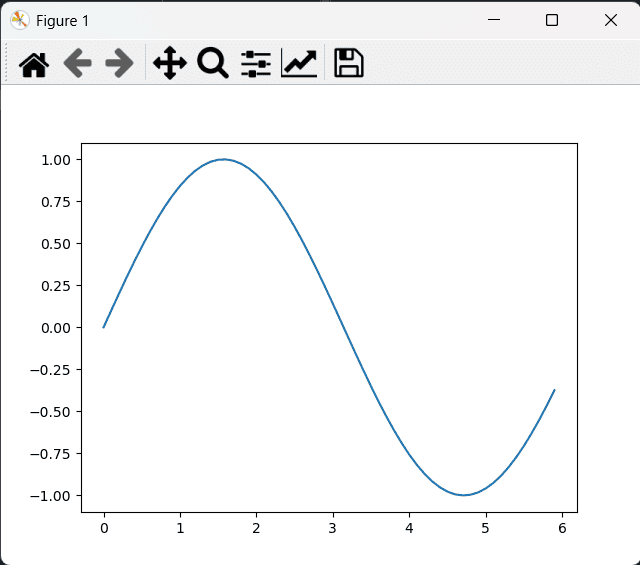
matplotlib
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.arange(0, 6, 0.1)
y = np.sin(x)
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.show()
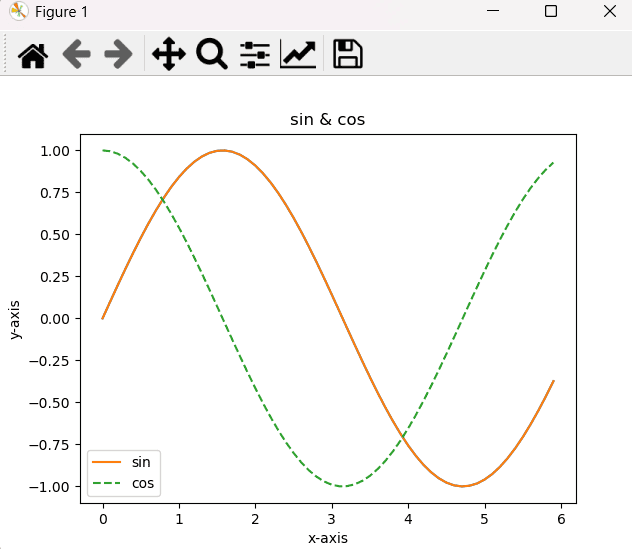
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.arange(0, 6, 0.1)
y1 = np.sin(x)
y2 = np.cos(x)
plt.plot(x, y1, label='sin')
plt.plot(x, y2, linestyle='--', label='cos')
plt.xlabel('x-axis')
plt.ylabel('y-axis')
plt.title('sin & cos')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
연습 문제
-
파이썬에서 딕셔너리로 선언하고자 한다. 적합한 것은?
1
me = {‘height’ : 180, ‘weight’: 70 }
-
다음 파이썬 프로그래밍에서 a[4]의 결과는?
1 2
a = [1,2,3,4,5] a[4]
a. 5
-
파이썬을 설치하기 위한 아나콘다 사이트는?
a. www.anaconda.com
-
Python 패키지를 설치하고 관리하는 프로그램이다. Dos 창에서 ( ) 안에 맞는 명령은?
1
C:\anaconda3>( ) install tensorflow
a. pip
-
다음과 같이 파이썬 함수 문을 작성하였다. hello2(“Jeong”) 의 결과는?
1 2 3 4
def hello2(object): print("Hello " + object + " !") hello2("Jeong")
a. Hello Jeong !