Servlet
- 김영한님의 스프링 MVC 1편 백엔드 웹 개발 핵심 기술 강의를 통해 Servlet의 HTTP 요청/응답 처리 메커니즘과 다양한 데이터 전송 방식을 정리함
Servlet 기본 설정
프로젝트 구성
- 필수 설정
- Java
- 17 이상
- Spring Boot
- 3.2 이상
- Packaging
- War (JSP 실행을 위해 필수)
- Dependencies
- Spring Web, Lombok
- Java
Servlet 등록
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
@ServletComponentScan // 서블릿 자동 스캔
@SpringBootApplication
public class ServletApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ServletApplication.class, args);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
@WebServlet(name = "helloServlet", urlPatterns = "/hello")
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
String username = request.getParameter("username");
response.setContentType("text/plain");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.getWriter().write("hello " + username);
}
}
HTTP 요청 로그 확인
1
logging.level.org.apache.coyote.http11=trace
- 주의사항
- 운영 환경에서는 성능 저하를 일으킬 수 있으므로 개발 단계에서만 사용
HTTP 요청 처리 아키텍처
요청 처리 흐름
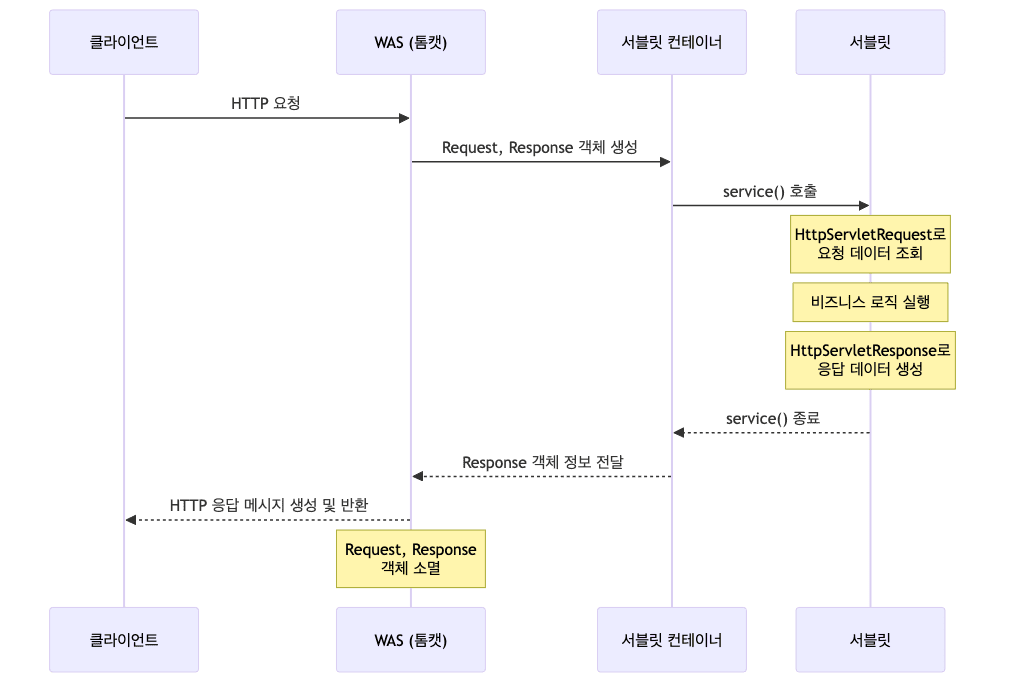
HttpServletRequest 구조
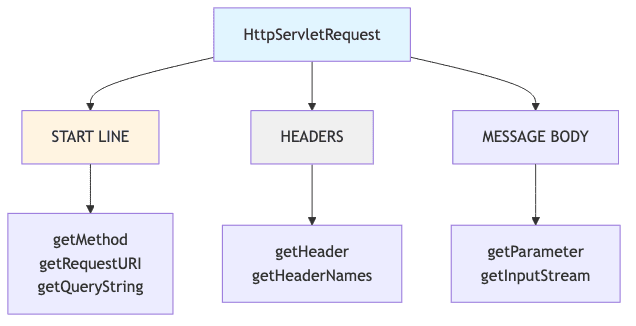
HTTP 요청 데이터 처리
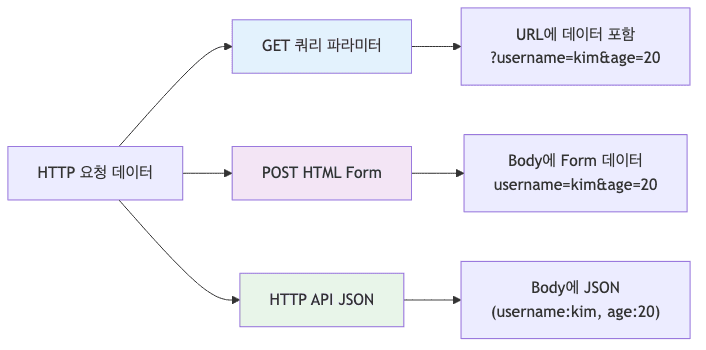
데이터 전송 방식 비교
| 방식 | Content-Type | 데이터 위치 | 사용 사례 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GET 쿼리 파라미터 | 없음 | URL 쿼리 스트링 | 검색, 필터, 페이징 |
| POST HTML Form | application/x-www-form-urlencoded | Message Body | 회원가입, 상품주문 |
| HTTP API (JSON) | application/json | Message Body | REST API, AJAX |
GET 쿼리 파라미터 처리
-
요청 예시
1
http://localhost:8080/request-param?username=hello&age=20
- 주요 API
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
// 단일 값 조회 String username = request.getParameter("username"); // 모든 파라미터 이름 조회 Enumeration<String> names = request.getParameterNames(); // Map으로 조회 Map<String, String[]> paramMap = request.getParameterMap(); // 복수 값 조회 (같은 이름의 파라미터가 여러개) String[] values = request.getParameterValues("username");
- 전체 코드 보기
POST HTML Form 처리
-
HTML Form
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <form action="/request-param" method="post"> username: <input type="text" name="username" /> age: <input type="text" name="age" /> <button type="submit">전송</button> </form> </body> </html>
-
HTTP 메시지 형식
1 2 3 4 5
POST /request-param HTTP/1.1 Host: localhost:8080 Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded username=hello&age=20
application/x-www-form-urlencoded형식은 쿼리 파라미터와 동일request.getParameter()로 GET/POST 구분 없이 조회 가능- Content-Type이 다르지만 서버는 동일한 방식으로 처리
HTTP API - 단순 텍스트
-
요청 예시
1 2 3 4
POST /request-body-string HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: text/plain hello world
-
서블릿 구현
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
@WebServlet(name = "requestBodyStringServlet", urlPatterns = "/request-body-string") public class RequestBodyStringServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { ServletInputStream inputStream = request.getInputStream(); String messageBody = StreamUtils.copyToString(inputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8); System.out.println("messageBody = " + messageBody); response.getWriter().write("ok"); } }
HTTP API - JSON
-
요청 예시
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
POST /request-body-json HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: application/json { "username": "hello", "age": 20 } -
데이터 클래스
1 2 3 4 5
@Getter @Setter public class HelloData { private String username; private int age; }
-
서블릿 구현
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
@WebServlet(name = "requestBodyJsonServlet", urlPatterns = "/request-body-json") public class RequestBodyJsonServlet extends HttpServlet { private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(); @Override protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { ServletInputStream inputStream = request.getInputStream(); String messageBody = StreamUtils.copyToString(inputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8); HelloData helloData = objectMapper.readValue(messageBody, HelloData.class); System.out.println("helloData.username = " + helloData.getUsername()); System.out.println("helloData.age = " + helloData.getAge()); response.getWriter().write("ok"); } }
HttpServletRequest 상세 API
Start Line 정보 조회
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
// HTTP 메서드
request.getMethod(); // GET
// 프로토콜
request.getProtocol(); // HTTP/1.1
// 스키마
request.getScheme(); // http
// 요청 URL (전체)
request.getRequestURL(); // http://localhost:8080/request-header
// 요청 URI (경로만)
request.getRequestURI(); // /request-header
// 쿼리 스트링
request.getQueryString(); // username=hello
// HTTPS 여부
request.isSecure(); // false
Header 정보 조회
1
2
3
4
// 모든 헤더 조회
request.getHeaderNames().asIterator()
.forEachRemaining(headerName ->
System.out.println(headerName + ": " + request.getHeader(headerName)));
1
2
3
4
5
6
host: localhost:8080
connection: keep-alive
user-agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 11_2_0)
accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml
accept-encoding: gzip, deflate, br
accept-language: ko,en-US;q=0.9
편의 메서드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
// Host 정보
request.getServerName(); // localhost
request.getServerPort(); // 8080
// Accept-Language 정보
request.getLocale(); // ko
// Cookie 정보
if (request.getCookies() != null) {
for (Cookie cookie : request.getCookies()) {
System.out.println(cookie.getName() + ": " + cookie.getValue());
}
}
// Content 정보
request.getContentType();
request.getContentLength();
request.getCharacterEncoding();
// Remote 정보 (클라이언트)
request.getRemoteHost(); // 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1
request.getRemoteAddr(); // 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1
request.getRemotePort(); // 54305
// Local 정보 (서버)
request.getLocalName(); // localhost
request.getLocalAddr(); // 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1
request.getLocalPort(); // 8080
HTTP 응답 처리
HttpServletResponse 역할
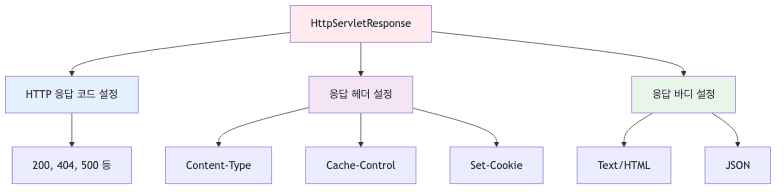
기본 응답 설정
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
@WebServlet(name = "responseHeaderServlet", urlPatterns = "/response-header")
public class ResponseHeaderServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
// 상태 코드 설정
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_OK); // 200
// 응답 헤더 설정
response.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/plain;charset=utf-8");
response.setHeader("Cache-Control", "no-cache, no-store, must-revalidate");
response.setHeader("my-header", "hello");
// 메시지 바디
response.getWriter().println("ok");
}
}
Content 편의 메서드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
// 기본 방식
// response.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/plain;charset=utf-8");
// 편의 메서드
response.setContentType("text/plain");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
// response.setContentLength(2); // 생략 가능 (자동 생성)
Cookie 설정
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
// 기본 방식
// response.setHeader("Set-Cookie", "myCookie=good; Max-Age=600");
// 편의 메서드
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("myCookie", "good");
cookie.setMaxAge(600); // 600초
response.addCookie(cookie);
Redirect 설정
1
2
3
4
5
6
// 기본 방식
// response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_FOUND); // 302
// response.setHeader("Location", "/basic/hello-form.html");
// 편의 메서드
response.sendRedirect("/basic/hello-form.html");
HTML 응답
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
@WebServlet(name = "responseHtmlServlet", urlPatterns = "/response-html")
public class ResponseHtmlServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
// Content-Type 필수 설정
response.setContentType("text/html");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println("<html>");
writer.println("<body>");
writer.println(" <div>안녕하세요</div>");
writer.println("</body>");
writer.println("</html>");
}
}
JSON 응답
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
@WebServlet(name = "responseJsonServlet", urlPatterns = "/response-json")
public class ResponseJsonServlet extends HttpServlet {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
// Content-Type 설정
response.setContentType("application/json");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
// 객체 생성
HelloData data = new HelloData();
data.setUsername("kim");
data.setAge(20);
// 객체를 JSON 문자열로 변환
String result = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(data);
// 결과: {"username":"kim","age":20}
response.getWriter().write(result);
}
}
- 주의사항
application/json은 UTF-8을 기본으로 사용application/json;charset=utf-8은 불필요한 파라미터response.getWriter()대신response.getOutputStream()사용 권장
- 전체 코드 보기
요청/응답 처리 패턴 비교
데이터 형식별 처리 방법
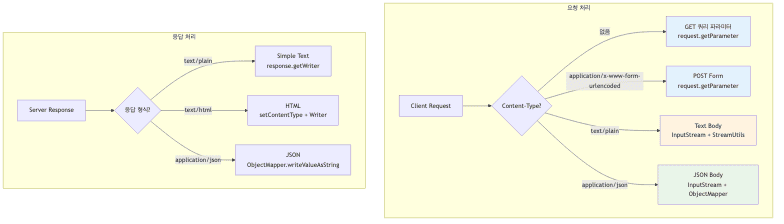
- 요청 처리 시 확인사항
- GET 쿼리 파라미터와 POST Form은
request.getParameter()동일 사용 - JSON 처리 시
ObjectMapper필수 - InputStream 읽을 때 Charset 명시 (UTF-8)
- 동일 이름 파라미터는
getParameterValues()사용
- GET 쿼리 파라미터와 POST Form은
- 응답 처리 시 확인사항
- Content-Type 반드시 설정
- HTML 응답은
text/html - JSON 응답은
application/json(charset 불필요)
- HTML 응답은
- Content-Length는 WAS가 자동 생성
- Content-Type 반드시 설정
연습 문제
-
서블릿이 HTTP 요청/응답 처리와 관련하여 주로 어떤 역할을 하는 걸까요?
a. HTTP 요청/응답 서버 구현
- 서블릿은 서버에서 HTTP 요청 메시지를 파싱하고, 필요한 비즈니스 로직을 처리한 후, HTTP 응답 메시지를 만들어 클라이언트에 되돌려주는 핵심 역할을 함
- 개발자가 편리하게 웹 서비스 요청/응답을 다루게 함
-
스프링 부트에서 별도의 웹 서버 설치 없이 서블릿을 실행할 수 있어 편리한 주된 기능은 무엇인가요?
a. 내장형 톰캣 서버 제공
- 스프링 부트는 내장형 톰캣 서버를 기본으로 포함하고 있어, 복잡한 웹 서버 설정 과정 없이 서블릿을 바로 실행하고 테스트하는 환경을 쉽게 만들어 줌
- 개발 생산성을 높여줌
-
HttpServletRequest객체를 사용하는 주된 목적은 무엇일까요?a. HTTP 요청 메시지 편리하게 읽기
- 개발자가 HTTP 요청 메시지의 시작 라인, 헤더, 바디 데이터를 직접 파싱하는 번거로운 작업 없이,
HttpServletRequest객체를 통해 표준화된 방법으로 정보를 쉽게 읽도록 돕는 도구임
- 개발자가 HTTP 요청 메시지의 시작 라인, 헤더, 바디 데이터를 직접 파싱하는 번거로운 작업 없이,
-
클라이언트가 서버로 데이터를 전송할 때, 일반적으로 HTTP 메시지 ‘바디’에 데이터를 포함시키는 방식은 무엇일까요?
a. GET 방식 (쿼리 파라미터)
- GET 방식의 쿼리 파라미터는 URL 자체에 데이터가 ‘키=값’ 형태로 표시되고, 바디는 보내지 않음
- 반면, POST, PUT, PATCH 등의 방식은 주로 데이터를 HTTP 메시지 바디에 담아 보냄
-
request.getParameter()메소드가 GET 방식 쿼리 파라미터와 POST 방식 HTML Form 데이터 모두 읽을 수 있는 이유는 무엇일까요?a. 데이터 형식이 ‘키=값’으로 같음
- GET 쿼리 파라미터와 POST HTML Form 데이터 모두 ‘키=값’ 형태의 URL 인코딩 방식으로 동일함
- 따라서 서버 입장에서는 데이터 형식이 같으므로
request.getParameter()메소드로 편리하게 읽을 수 있음
-
서버 간 통신, 모바일 앱 통신 등에서 HTTP 메시지 바디에 직접 데이터를 담아 전송할 때 주로 사용하는 HTTP 메소드는 무엇일까요?
a. POST, PUT, PATCH
- API 통신에서 HTTP 메시지 바디에 JSON 등의 데이터를 담아 보낼 때는 주로 리소스 생성(POST), 전체 업데이트(PUT), 부분 업데이트(PATCH) 등의 메소드를 사용함
-
서버 측에서 수신한 JSON 형식 HTTP 메시지 바디 데이터를 편리하게 자바 객체로 변환하기 위해 필요한 것은 무엇일까요?
a. JSON 파싱 라이브러리
- HTTP 메시지 바디의 JSON 데이터는 단순 텍스트 형태이므로, 이를 자바 객체 번드로 자동으로 매핑해주는 Jackson과 같은 JSON 파싱 전용 라이브러리가 서버 애플리케이션에 필요함
-
서블릿에서 클라이언트로 보내는 HTTP 응답 메시지의 상태 코드(예: 200 OK, 404 Not Found)를 설정하는 메소드는 무엇일까요?
a.
response.setStatus()- HTTP 응답의 상태 코드는 요청 처리 결과를 나타내며,
response.setStatus()메소드를 사용하여 200(성공), 400(잘못된 요청), 404(찾을 수 없음) 등의 코드를 설정할 수 있음
- HTTP 응답의 상태 코드는 요청 처리 결과를 나타내며,
-
HTTP 응답으로 텍스트나 HTML 콘텐츠를 보낼 때, ‘UTF-8’ 과 같은 문자 인코딩을 올바르게 설정하는 것이 중요한 주된 이유는 무엇일까요?
a. 문자 깨짐 없이 올바르게 표시
- 응답 데이터의 문자 인코딩을 명확히 지정하지 않으면, 클라이언트 브라우저가 서버의 의도와 다르게 문자를 해석하여 ‘깨짐’ 현상이 발생할 수 있음
- 특히 다양한 언어 사용 시 중요함
-
HTTP 응답 메시지 바디에 JSON 형식 데이터를 담아 보낼 때, 응답 헤더에 설정해야 하는 Content-Type 값은 무엇일까요?
a.
application/json- 클라이언트에게 응답 메시지 바디에 담긴 데이터의 형식이 JSON임을 알려주기 위해
Content-Type헤더를application/json으로 설정해야 함 - 이는 표준 명세에 정의되어 있음
- 클라이언트에게 응답 메시지 바디에 담긴 데이터의 형식이 JSON임을 알려주기 위해
요약 정리
- Servlet의 역할
- TCP/IP 연결 관리
- HTTP 메시지 파싱
- HttpServletRequest/Response 객체 생성
- 서블릿 생명주기 관리
- 멀티스레드 처리
- 요청 데이터 조회
- 파라미터 조회 (GET, POST Form):
request.getParameter("name") - 바디 조회 (Text, JSON):
request.getInputStream()
- 파라미터 조회 (GET, POST Form):
- 응답 데이터 설정
- 상태 코드
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_OK)
- 헤더
response.setContentType("application/json")
- 바디
response.getWriter().write("content")
- 상태 코드
- 로깅
- 개발 환경에서만 trace/debug 사용
- 인코딩
- UTF-8을 명시적으로 지정
- JSON 처리
- Jackson ObjectMapper 활용
- 예외 처리
- ServletException, IOException 처리